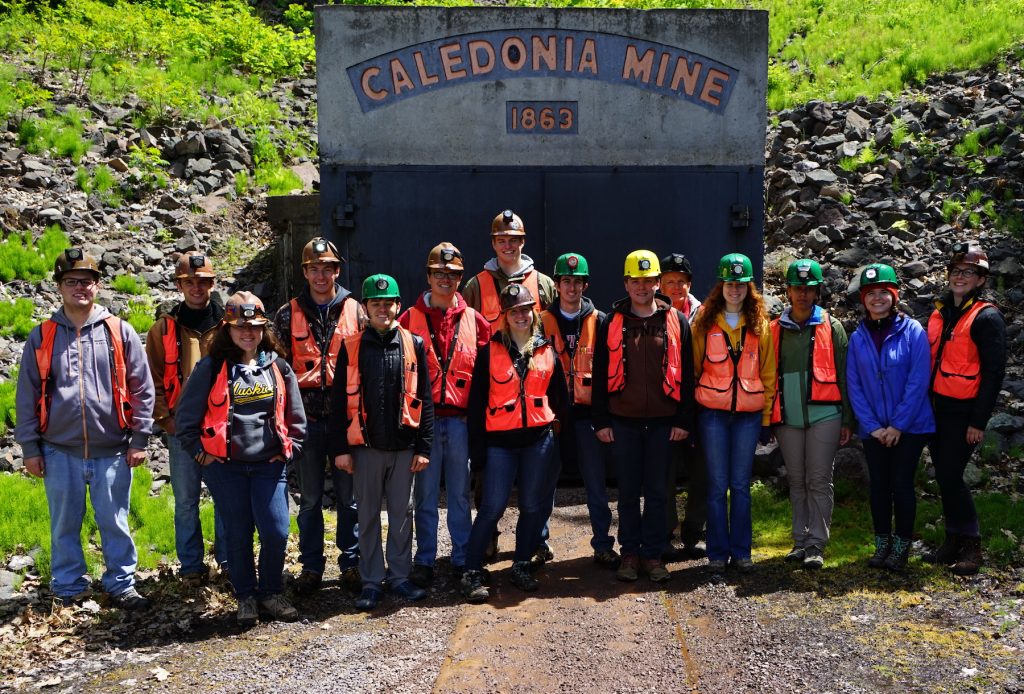
A total of 13 high school students from throughout Michigan are participating in a 5-day internship at Michigan Tech July 15-19, 2019. Faculty and their graduate students voluntarily host the students in engaging research activities during the week. The faculty’s department, along with the College of Engineering and College of Sciences and Arts, together provide a $600 scholarship for the student that covers their transportation, lodging and meals.
The interns work with Michigan Tech faculty and graduate students in their research lab or doing field work outside. During the week, students tour the Michigan Tech campus and local area, ‘experience college living’ in a residence hall, and meet students from across Michigan and beyond!
In Dr. Parisa Abadi’s Mechanical Engineering Lab, students will be 3D printing nanomaterials. Dr. Tara Bal in the School of Forest Resources and Environmental Sciences (SFRES) will conduct invasive species monitoring and forest health assessments. Dr. Will Cantrell in Atmospheric Physics will have the intern investigating why some clouds rain, while others do not.
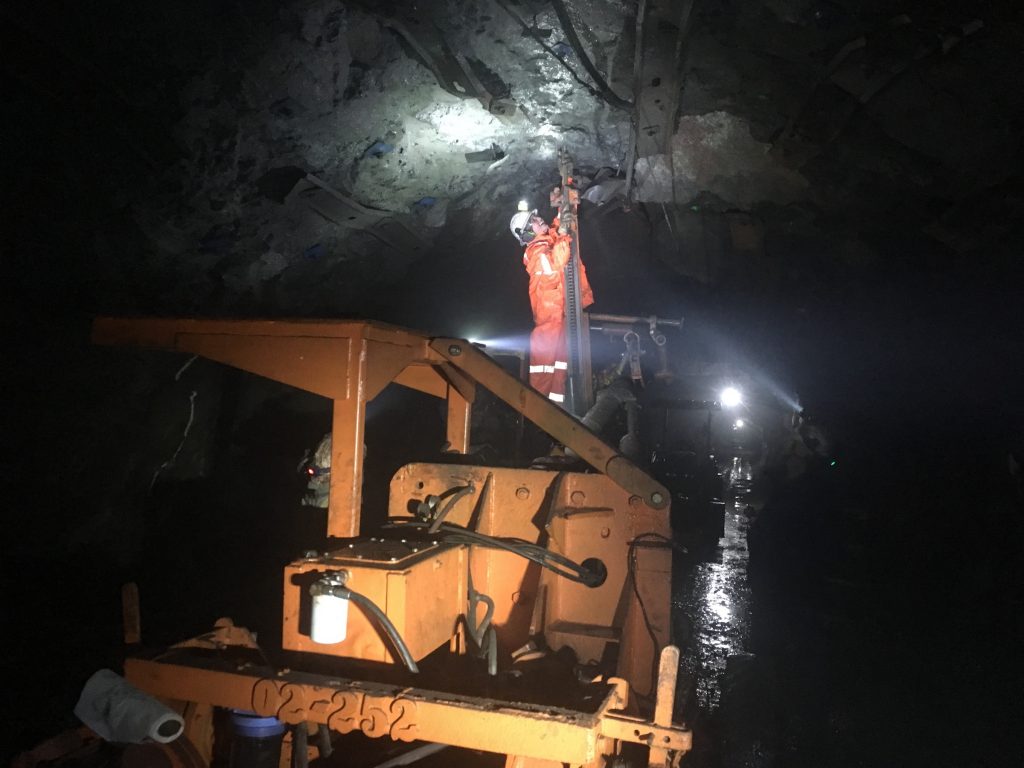
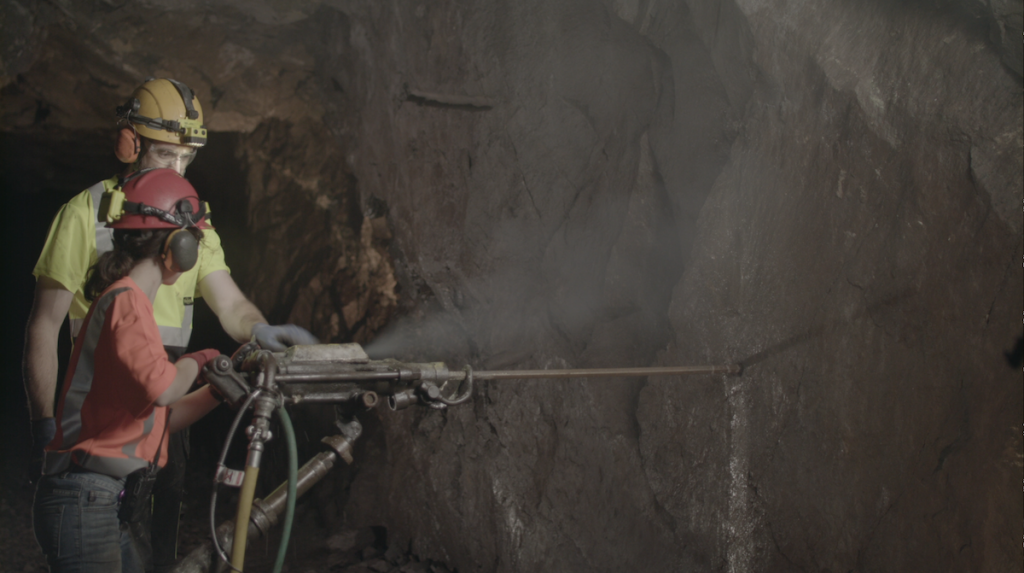
Dr. Daniel Dowden in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) has his intern investigating which technologies will allow buildings to sustain minimal damage and be easily repairable after large earthquakes. Four faculty–Drs. Deering, Waite, Oommen, and Gierke in Geological and Mining Sciences and Engineering are providing a broad introduction of mapping geological features, conducting geophysical surveys, and working to construct a 3-D model of a geological feature. Dr. Casey Huckins and graduate student–Chris Adams in Biological Sciences–are monitoring Pilgrim River and measuring the results of a fish survey in the lab. Dr. Daisuke Minakata in CEE and Dr. Paul Doskey in SFRES, along with graduate students, are researching innovative drinking water and wastewater treatment technologies.
Dr. Michael Mullins in the Department of Chemical Engineering (ChE) has his intern researching ways to remove PFAs contaminants from water. Dr. Rebecca Ong in ChE has her two interns investigating biofuel production from native grasses. Dr. Chelsea Schelly in the Department of Social Sciences and Dr. Robert Handler in the Sustainable Future Institute are measuring food, energy, and water consumption in residential homes and looking for ways to reduce household resource consumption. Dr. Kuilin Zhang and his graduate student Qinjie Lyu in CEE have their intern studying traffic data collection, traffic signal timing, eco-driving, and using traffic simulation software.
The program is coordinated by the Michigan Tech Center for Science and Environmental Outreach, in partnership with Summer Youth Program who provides logistical support and supervises the students in the residence halls in the evening.
Funding for the program is received from the Michigan Tech College of Engineering, the College of Sciences and Arts, the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, the Department of Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics, the Department of Chemical Engineering, the School of Forest Resources and Environmental Science, the Department of Biological Sciences, the Great Lakes Research Center, Youth Programs, and an anonymous donor.
The STEM internship program is coordinated by Joan Chadde at Michigan Tech Center for Science and Environmental Outreach.