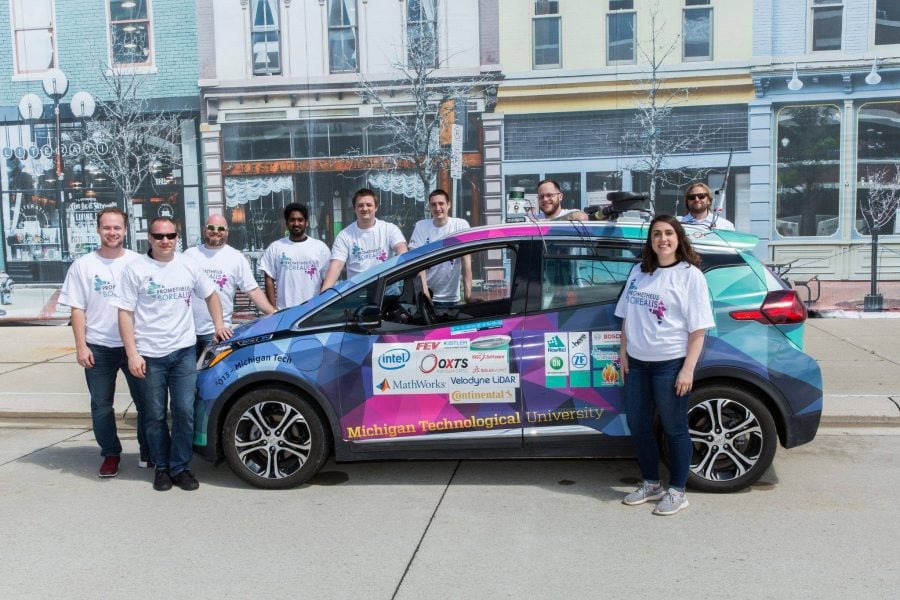
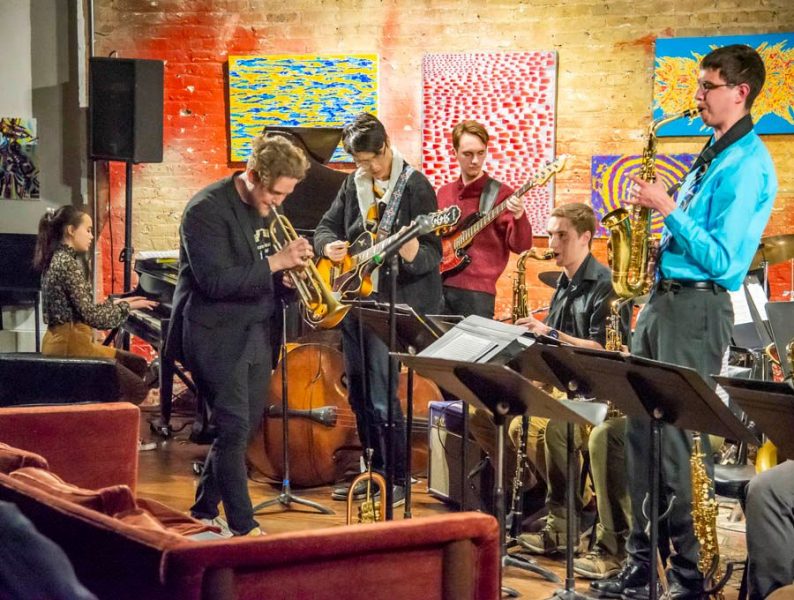
Jeremy Bos and Darrell Robinette, mentors and advisors of Michigan Tech’s SAE Autodrive Challenge (and both Michigan Tech alums) share their knowledge on Husky Bites Live, on campus in the Rozsa Center at Alumni Reunion 2021. The session takes place Friday, August 6 at 1:30 pm ET. Everyone in attendance will learn something new, with time after for Q&A.
Can’t make it in person? Join us remotely. We’ll share a link to join the Zoom webinar on the Alumni Reunion website as the event draws near. Afterwards (weather permitting) you’re invited to join us out on the Walker Lawn. Meet the students of Prometheus Borealis and Robotics Systems Enterprise, get a close look at their autonomous vehicles—and be sure to bring your questions.
It’s a wild ride.
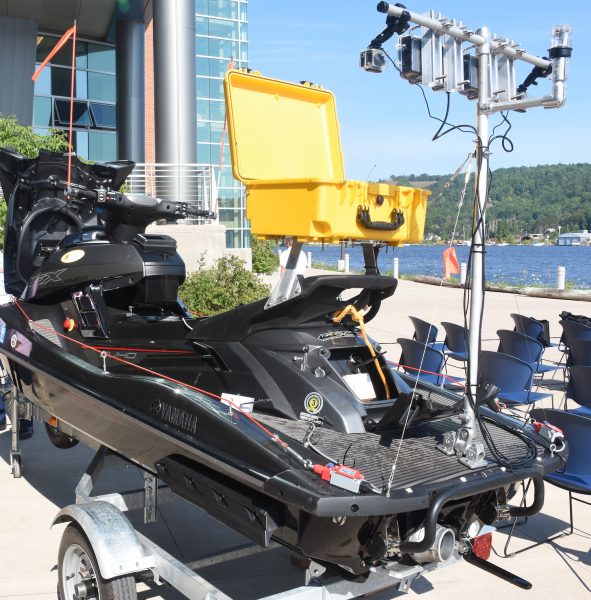
Starting with a Chevy Bolt, Michigan Tech students outfit it with sensors, control systems and computer processors to successfully navigate an urban driving course in automated driving mode. And, test it in blizzard conditions!

It’s also an ambitious project with an equally ambitious goal: Three years of the competition, with increasing levels of autonomy and more difficult challenges in each successive year.
Michigan Tech’s team is Prometheus Borealis, after Prometheus, the Greek deity responsible for bringing technology to people, and Boreas, the purple-winged god of the north wind.The SAE Autodrive Challenge competition is jointly sponsored by General Motors (GM) and the Society of Automotive Engineers International (SAE).

“The competition focuses on the electrical engineering, computer engineering, robotics engineering, and computer science skills needed to implement the sensors, signal processing and artificial intelligence needed to make the car drive itself,” says team co-advisor, ECE Assistant Professor Jeremy Bos. “Mechanical engineers and a wide range of other disciplines are represented on the teams, as well.”
ME-EM Assistant Professor Darrell Robinette is the team’s other co-advisor. Robinette worked as an engineer at GM for 9 years before joining Michigan Tech in 2014, with roles in transmission, NVH, electrification and calibration engineering groups. He is a longtime First Robotics Competition mentor, too.
Bos earned his BS at Michigan Tech in 2000, and returned to earn his PhD in 2012, both in Electrical Engineering. Robinette earned a BS in 2004 and a PhD in 2007, both in Mechanical Engineering.
Student-driven Autonomy
On the student side, the AutoDrive Challenge project is spearheaded by Robotic Systems Enterprise (RSE), also advised by Bos and Robinette. RSE is part of Michigan Tech’s award-winning Enterprise program. “It’s one of the best places on campus to learn robotics,” says Bos. The team’s many projects come in many shapes and sizes, from designing a vision system for work with a robotic arm, to an automatic power management system for weather buoys. Clients include Ford Motor Company and Michigan Tech’s Great Lakes Research Center.
SAE Autodrive Challenge Final Results

The four-year challenge wrapped up on June 14 with Michigan Tech’s Prometheus Borealis team earning 3rd place overall, bringing home the second most trophies. Teams from University of Toronto and University of Waterloo earned first and second overall. Read the full results on the SAE Autodrive Challenge website.
Teams from eight North American universities competed: Michigan Technological University, Michigan State University, Kettering University, University of Waterloo, University of Toronto, Texas A&M University, Virginia Tech, North Carolina A&T State University
“We’re going to need a bigger trophy case.”
Next Up: Autodrive Challenge II
Also in June, SAE International and General Motors (GM) announced 10 collegiate teams selected to compete in AutoDrive Challenge II. Michigan Tech was on the list.

The competition continues the strong collaboration between GM and SAE in STEM education and will build on the groundbreaking success of the first iteration of AutoDrive Challenge. Teams will develop and demonstrate an autonomous vehicle (AV) that can navigate urban driving courses as described by SAE J3016™ Standard Level 4 automation.
The following 10 university teams will participate in AutoDrive Challenge II:
Kettering University, Michigan Technological University, North Carolina A&T State University, The Ohio State University, Penn State University, Texas A&M University
University of Toronto, University of Wisconsin – Madison, Queens University and Virginia Tech.
“At General Motors, we envision a future of zero crashes, zero emissions and zero congestion, and we have committed ourselves to leading the way toward this future,” said Dan Nicholson, GM vice president, global electrification, controls, software and electronics and executive sponsor of the competition.

“The AutoDrive Challenge is a great way to give students the hands-on experience they need to find success,” he adds. “We are very excited to work with these talented students over the course of the competition and know they will make an immediate impact on the automotive industry upon graduation.”
“Michigan Tech’s SAE AutoDrive Challenge team has proven our students innovate to succeed.”
Dr. Robinette, how did you first get started in engineering? What sparked your interest?

When I was 5, my dad took me for a tour at his place of work, Detroit Edison’s Belle River Powerplant. It was awe inspiring seeing all the equipment and getting an explanation of how it worked and what it did. Pretty amazing that they hang the boilers from the ceiling, eh? Everything at the plant was just so cool, especially the controls and control room.
My dad introduced me to all the engineers he worked with, and all of them were MTU grads. They played a part in encouraging me where to go for engineering, even though I was only 5 years old. My dad gave me a Babcock & Wilcox Steam book after the visit. Even though I didn’t understand all the engineering in it at the time, pictures of the power plant equipment, construction, assemblies all caught my interest.
Also, like most engineers, l played with Legos during childhood. Lots and lots of Legos to build whatever my imagination could create.
Family, home, hobbies?
I go mountain biking whenever I can, also wake surfing, snowboarding, and cross country skiing. My wife, Tara, is an MTU alumna (Pre-Med/Biology ‘07). She is one of the Emergency Room physicians at Portage Health Hospital. We have two daughters: Adelyn, 3, and Amelia, one. I like building, tinkering and fixing (typical mechanical engineer stuff), and trying to be a super dad for my girls.
Dr. Bos, how about you? When did you first get into engineering? What sparked your interest?

My Dad ran a turn-key industrial automation and robotics business throughout most of my childhood. In fact, I got my first job at age 12 when I was sequestered at home with strep throat. I felt fine, but couldn’t go to school. My Dad put me to work writing programs for what I know now are Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs); the ‘brains’ of most industrial automation systems.
I really liked these new things called ‘personal computers’ and spent quite a bit of time programming them. By the time I was in high school I was teaching classes at the local library on computer building, repair, and this other new thing called ‘The Internet’. I ended up in engineering because I like to build things (even if only on a computer) and I like to solve problems (generally with computers and math).
What do you like to do in your spare time?
I live in Houghton with my wife and fellow alumna, Jessica (STC ’00). We have a boisterous dog, Rigel, named after a star in the constellation Orion, who bikes or skis with me on the Tech trails nearly every day. When I have time I also like to kayak, and stargaze.
Learn More About Husky Bites


Launched by Dean Janet Callahan in 2020 near the start of the pandemic, Husky Bites is an interactive Zoom webinar that takes place each fall and spring.
During the semester, every Monday at 6, rach “bite” is a suppertime mini-lecture, presented by a different Michigan Tech faculty member, who weaves in a bit of their own personal journey, and brings a co-host, as well—an alum or a current student who knows a thing or two about the topic at hand.
The Husky Bites weekly Zoom webinar series resumes starting Monday, Sept. 13.
“We’ve had attendees from nine countries, and a great mix of students, alumni, our Michigan Tech community and friends,” says Dean Callahan, who mails out prizes for (near) perfect attendance.
Get the full scoop at mtu.edu/huskybites.