Michigan Tech is offering both a in-person and online certificate in the Foundations of Cybersecurity. In nine credits, students will learn how to identify and describe the foundational principles of securing both a computer system and a computer network. They’ll also study the fundamentals of secure software development and apply them effectively.
This credential addresses cyber crime, a costly and dangerous global problem.
Brief Case Study: The WannaCry Ransomware Attack
Flash backward to seven years ago.
In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware worm spread rapidly across computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system.
This worm first encrypted files and then demanded ransomware payments–first 300$ and then 600$ in bitcoins. Unfortunately, even those who paid the ransom, such as a friend of this writer, still lost their files.
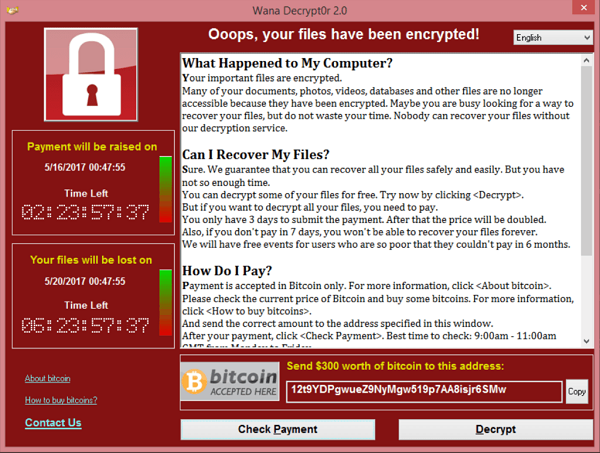
How did this attack happen? The worm wriggled its way in through a vulnerability in Windows’ Server Message Block (SMBv1) protocol (EternalBlue), used for file and printer sharing on Windows networks. Then, it installed DoublePulsar as the “backdoor” on compromised computers.
The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) had previously disclosed the Eternal Blue weakness. Then, a hacking group called the Shadow Brokers leaked it onto the web and cyber criminals took lurking in the shadows took notice. Within a few days, WannaCry affected at least 200,000 computers and 300,000 devices in more than 150 countries. The attack caused widespread disruption, particularly in critical sectors such as healthcare, telecommunications, and manufacturing. One of the most notable victims was the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), which canceled both appointments and operations, turning patients away.
Microsoft quickly released security patches for versions of Windows with the Eternal Blue vulnerability. However, it had actually sent security patches two months earlier, which hadn’t taken effect because many organizations hadn’t taken the time to update their systems. Oops!
Training in the Foundations of Cybersecurity is Needed Now More Than Ever.
This attack, then, not only underscored the importance of updating systems regularly to install timely security patches, but also the need to quickly implement protocols of backup and recovery. Even more so, WannaCry revealed the demand for more well-trained, cybersecurity professionals from government agencies, private sector companies, and other organizations who could collaborate on and react quickly to global cyber crime incidents.
Along with ransomware, cybersecurity professionals must be ready to battle Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), Phishing and Social Engineering, Zero-day attacks, high-profile data breaches, DDoS attacks, and many other types of cyber crime. The changing nature of cyber threats also requires organizations to continually improve their defenses and adapt to new attack vectors.
And digital transformation, vehicle electrification, robotic workplaces, and Industry 4.0 pose new challenges as well. That is, as organizations move to cloud environments and the IoT (Internet of Things) continues to proliferate, cybersecurity professionals must safeguard infrastructures and predict possible vulnerabilities.
More troubling news: In the last decade or so, cyber attacks have grown in sophistication, frequency, and size. In fact, according to US News, “Data breaches and ID theft are still hitting records.” Recently, on July 4, while this blog was being drafted, Cybernews reported that a file containing 9,948,575,739 plain text passwords was posted on a hacker site by the user Obamacare. This file, known as the RockYou24 leak, was a compilation of passwords that were collected from 4000 databases over the last two decades. (Previously, the RockYou21 leak contained 8.5 billion of these same passwords.)
With these passwords, Cybernews explains that “threat actors could exploit the RockYou2024 password compilation to conduct brute-force attacks and gain unauthorized access to various online accounts used by individuals who employ passwords included in the dataset.”
Here are Some Other Startling Statistics About Cyber Crime:
- $4.45 million = average global cost of a data breach
- 533,000,000 = number of accounts leaked in 2021 Facebook data breach
- 353,027,892 = number of people affected by data breaches in 2023
- 5.4 million = number of personal data breaches in 2022
- 2,563,959 = personal reports of fraud in 2022
The Cybersecurity Talent Gap is Expanding.
But perhaps one of the biggest challenge that cybersecurity professionals face is that there are not enough of them. That is, many organizations are struggling to fill critical positions. The global cybersecurity employment gap, which reached 4 million workers in 2023 (ISC2 2023), is expected to expand to 85 million by 2030.
The United States is one of those countries facing a shortage of cybersecurity professionals.
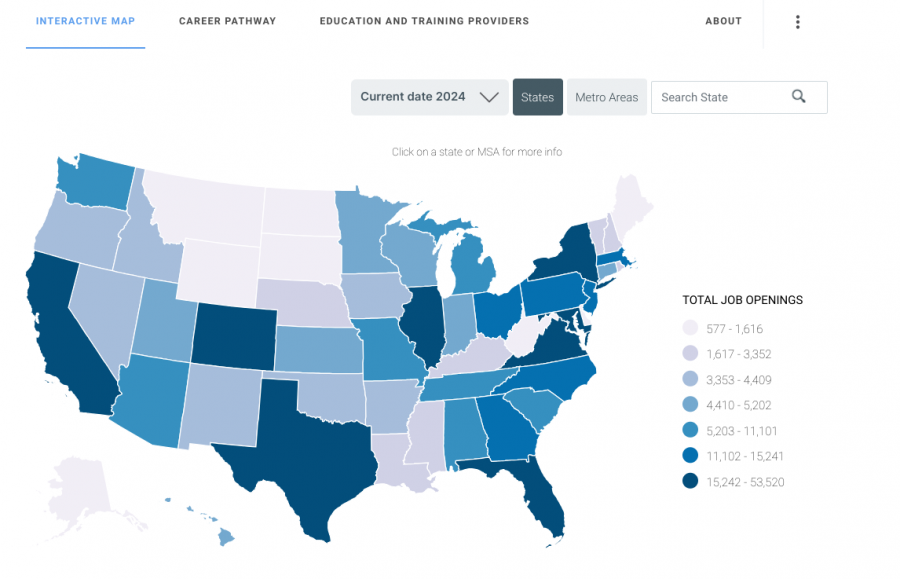
Between September 2022 and August 2023, 572,000 US jobs opened up in the cybersecurity industry. This number is up 74% from 2010.
And in the US, there were 1.18 million cybersecurity professionals employed between September 2022 and August 2023, which is also an an increase of 59% since 2010.
To help address this talent shortage, Michigan Tech is offering both online and in-person certificates in the Foundations of Cybersecurity, which start in Fall 2024. Students can complete this certificate or use the credits to dive deeper into cybersecurity and progress towards a master’s degree. They can choose from either Michigan Tech’s MS in Cybersecurity or the MS in Computer Science.
To be eligible for the program, applicants must have earned an undergraduate degree in computer science, computer engineering, or software engineering. The online application is free and requires no GMAT or GRE.
This certificate adds to the roster of MTU’s already respected cybersecurity research program, recognized nationally for its academic and research excellence. In fact, the US National Security Agency designated MTU as a National Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber Research (CAE-R). This CAE-R designation, establishing that Michigan Tech has met the rigorous requirements set forth by the NSA, extends through the 2029 academic year.
The Future Looks Bright for Those with Skills in the Foundations of Cybersecurity.
When it comes to cybersecurity professionals, there are several possible career paths.
Take the career of Information Security Analyst, for instance. A person in this role will have several responsibilities. They must use and maintain software, such as firewalls and data encryption programs, to protect sensitive information. In addition, they must check for vulnerabilities in computer and network systems; research the latest information technology (IT) security trends; and prepare reports that document general metrics, attempted attacks, and security breaches.
Being vigilant and proactive are also essential traits of this cybersecurity professional as they strive to develop security standards and best practices for their organization and timely recommend security enhancements. And they are also heavily involved with creating their organization’s disaster recovery plan, which IT employees must follow in case of emergency.
Because of the importance of these tasks, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a need for several tens of thousands of these analysts, with a career growth of 32% (much faster than average.) And these jobs way well, too: the 2023 median salary of an information security analyst was $120,360.
Other Top-Paying Cybersecurity Jobs
- Cybersecurity Analyst: $114,306
- Cybersecurity Manager: $150,943 per year
- Penetration and Vulnerability Tester: $124,424
- Cybersecurity Architect: $147,142 per year
- Cybersecurity Engineer: $131,768
- Incident and Intrusion Analyst: $103,639
- Cybersecurity Consultant: $124,275
- Cyber Crime Analyst: $103,198

Educate Yourself to Meet the Growing Need for Cybersecurity Professionals.
The estimated loss of that 2017 WannaCry incident was about four billion dollars. That bill was just a drop in the bucket.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, cyber crime is expected to grow by 15% a year in the next three years. What this prediction means is that cyber crime will cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This figure includes damage and destruction of data, stolen money, lost productivity, theft of intellectual property, and other costs.
Professionals with training in the foundations of cybersecurity can not only save organizations a lot of money, then, but even save lives.
Yes lives. When a 2020 ransomware attack on Dusseldorf University Hospital (Germany) caused its IT systems to fail (30 servers!), the hospital could not admit emergency patients. As a result, staff directed a critically ill woman who needed immediate care to another hospital about 20 miles away. This delay in treatment, which contributed to the patient’s death, is often cited as the first death resulting from a cyber attack.
It is obvious that the costs of cybercrime , which are immense, multifaceted, and global, impact economies, organizations, and individuals. Because of these costs, cybersecurity professionals are needed across every sector and industry. But there is a particularly urgent need for them in financial services, health care, government, national security, manufacturing, and retail.
And the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the increasing reliance on digital technologies suggest that these costs will continue to rise, highlighting the crucial demands for both robust cybersecurity measures and the highly skilled and trained professionals to enact them.