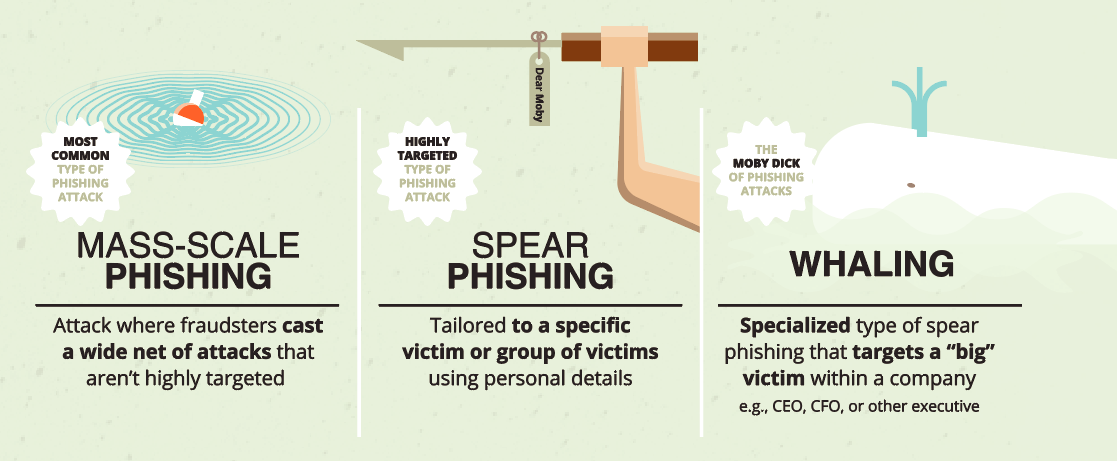
There’s more than one way to be phished!
Cybercriminals use types of social engineering—manipulating people into doing what they want—as the most common way to steal information and money. Social engineering is at the heart of all types of phishing attacks—those conducted via email, SMS, and phone calls. Technology makes these sorts of attacks easy and very low risk for the attacker. Make sure you’re on the lookout for these variants on the traditional, mass emailed phishing attack:
- Spear phishing: An attack of this kind often involves very well-crafted messages that come from what looks like a trusted VIP source, often in a hurry, targeting those who can conduct financial transactions on behalf of your organization (sometimes called “whaling”).
- SMiShing: Literally, phishing attacks via SMS, these scams attempt to trick users into supplying content or clicking on links in SMS messages on their mobile devices. Flaws in how caller ID and phone number verification work make this an increasingly popular attack that is hard to stop.
- Vishing: Voice phishing, these are calls from attackers claiming to be government agencies such as the IRS, software vendors like Microsoft, or services offering to help with benefits or credit card rates. Attackers will often appear to be calling from a local number close to yours. As with SMiShing, flaws in how caller ID and phone number verification work make this a dangerous attack vector.
No matter the medium, follow these techniques to help prevent getting tricked by these social engineering attacks:
- Don’t react to scare tactics: All of these attacks depend on scaring the recipient, such as with a lawsuit, that their computer is full of viruses, or that they might miss out on a chance at a great interest rate. Don’t fall for it!
- Verify contacts independently: Financial transactions should always follow a defined set of procedures, which includes a way to verify legitimacy outside email or an inbound phone call. Legitimate companies and service providers will give you a real business address and a way for you to contact them back, which you can independently verify on a company website, support line, etc. Don’t trust people who contact you out of the blue claiming to represent your company.
- Know the signs: Does the message/phone call start with vague information, a generic company name like “card services,” an urgent request, and/or an offer that seems impossibly good? Hang up or click that delete button!
Related resources to check out
- Learn more about spam and phishing or hacked accounts from the National Cyber Security Alliance.
- Read this Better Business Bureau Tip on Phishing Scams.
- Read the FCC article on Avoiding the Temptation of SMiShing Scams
- The FTC provides more information for consumers about phone scams and how to spot them.
- See our previous Campus Security Awareness Campaign blogs about phishing and ransomware: October 2018: Don’t Let a Phishing Scam Reel You In, February 2017: Learn What It Takes to Refuse the Phishing Bait, September 2017: Avoiding Ransomware Attacks, and April 2016: Don’t Get Hooked
Campus Security Awareness Campaign 2019
This content is from a larger campaign designed to support security professionals and IT communicators as they develop or enhance their security awareness plans. The campaign is brought to you by the Awareness and Training Working Group of the EDUCAUSE Higher Education Information Security Council (HEISC).