A robotic guard dog (or robodog) stationed in an abandoned warehouse relentlessly chases intruders across a barren, post-apocalyptic landscape. Armed with tracking weapons, highly sophisticated sensors, and artificial intelligence, this robodog does not give up its hunt easily.
To avoid spoilers, that is about all I will say about “Metalhead,” the fifth, and arguably, most terrifying episode of season one of the series Black Mirror. Although many have debated the episode’s meaning, one possible interpretation is a gruesome picture of what might happen if evolved, intelligent, unchecked robots ruled the workplace. And if they took their jobs, well, maybe a little too seriously.
The good news is that there are currently no rogue robodogs guarding warehouses and going on killing sprees. However, robots have been in industry for half a century. The effects of this integration, though certainly less sinister, have troubled a few. That is, one of the most popular searches on Google is this question or variations of it: “Will robots take our jobs?”
The answer is complicated: yes, no, and they already have. And the situation might be better or worse than you think.
Making Manufacturing Easier
When many of us contemplate robots in the workplace, we might think of Amazon. This company operates over 100,000 robots on its various factory floors. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) pick, sort, and transport orders; robotic arms pack items; and autonomous ground vehicles navigate the huge warehouses.
However, on the global stage, Amazon is somewhat of a bit player. FoxConn, a Chinese electronics manufacturer, currently has over 300,000 robots in use for assembling its products. These robots help create phones, computers, tablets, and gaming consoles for companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Samsung.
But the electronics industry was not the first to integrate robots into the workplace: the automotive industry was. It took a chance on and then popularized the first industrial robot: Unimate.
Unimate was the creation of Joseph Engelberger, whom many call the father of robotics. Inspired by Isaac Asimov and his vision of robot helpers, Engelberger strove to create robots that would improve manufacturing while making workers’ lives easier.
In 1959, General Motors installed the first prototype of Unimate #001 in its Trenton, New Jersey plant. Weighing a whopping 2700 pounds, this robot’s primary job was diecasting.
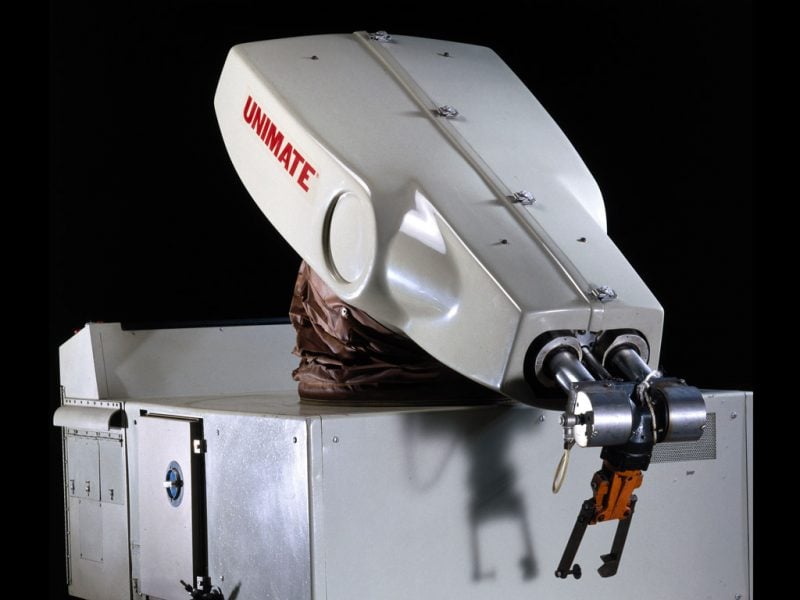

And only a decade later, GM’s rebuilt factory in Lordstown, Ohio, housed an army of spot-welding robots. These robots could build 110 cars an hour, which was double the manufacturing rate at that time.
Choosing the Right Robots for the Job (or Jobs)
An automated machine that does just one thing is not a robot. It is simply automation. A robot should have the capability of handling a range of jobs at a factory.
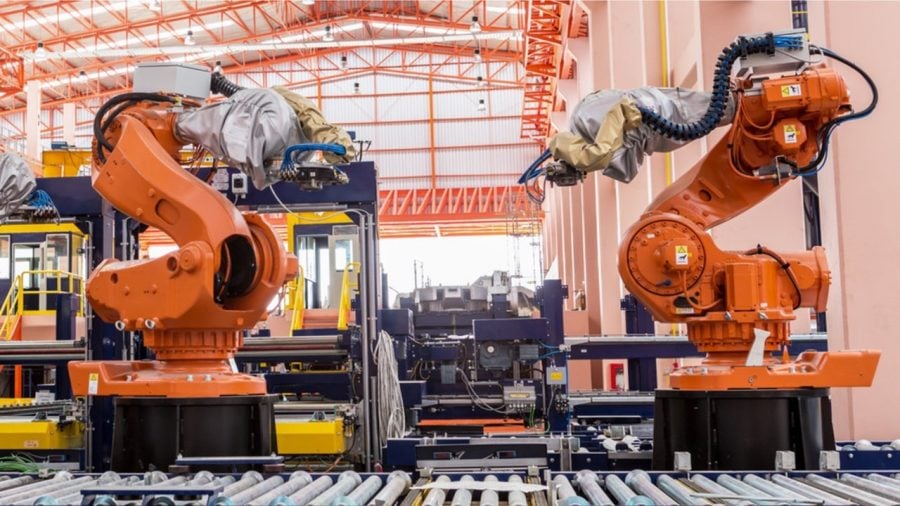
Perhaps Engelberger’s dream is best satisfied by articulated robots, equipped for several jobs. With their flexibility, dexterity, and reach, these robots are adept at assembling, packaging, palletizing, welding, and more. Palletizing robots perhaps perform one of the most annoying and dangerous of tasks in a warehouse environment: stacking stuff. These hefty robotic arms spend all day neatly piling items onto pallets.
Other common robots include SCARA (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm). SCARAs perform actions between two parallel planes or assemble vertical products. Delta (spider robots) excel at high-speed actions involving light loads.
And then there are Cartesian robots, or gantry robots. They “have an overhead structure that controls the motion in the horizontal plane and a robotic arm that actuates motion vertically. They can be designed to move in x-y axes or x-y-z axes. The robotic arm is placed on the scaffolding and can be moved in the horizontal plane.” It also has an effector or machine tool attached to its arm, depending on its function. This article goes into greater detail about the four types of robots that manufacturers should know and use.
The automotive industry (as does much of manufacturing) uses robots to spot-weld, pick, paint, and palletize–boring, yet dangerous jobs. Jeff Moore, Volvo’s vice president of manufacturing in the Americas, says that welding, “with all the heat and sparks and high current and things is a natural spot to be looking at where you can more heavily automate.” However, for intricate work on the assembly line, such as attaching hoods, bumpers, and fenders, “the human touch has a lot of advantages.”
Integrating Robots and Automation
But these metal workers do not just assemble cars and create heavy-duty products. Robots and automation also assist in other industries, such as in agriculture and food production.
Helping With Agriculture and Food Production
In agriculture, for instance, robots may plant, harvest, spray crops, control weeds, analyze soil, and monitor crops. And when it comes to agricultural equipment, some of the biggest players are John Deere, AGCO, CNH Industrial, and Kubota. These companies are also investing in robotics and automation; as well as tractors, drones, and data analytics to improve efficiency and crop yield and to reduce costs. Recently, for instance, Trimble and Horsch collaborated to build an autonomous sprayer.
And in food production, robots might slice, package, and label products at a much more rapid rate than humans. For instance, the global food production and processing company Cargill heavily uses robotic automation. It invented the first robotic cattle herder. Cargill and Tyson Foods, in fact, are also moving heavily into automation and cobots for meat production.

In one of the more famous and humorous episodes of I Love Lucy, Lucy and Ethel get employment at a candy factory. Their job: keeping up with increasing production and quickly wrapping candy as it rolls down the belt. They fail miserably as the line picks up, shoving candy in their mouths, their pockets, and even their dresses. Well, thanks to robots, inadequately trained (and slower than ideal) humans will no longer have to keep pace by eating the profits. Their tasks might be made easier by cobots.
Recently, “cobots” or modular, agile, collaborative robots have been the focus of robot manufacturers. Rather than replace workers, cobots work alongside their human employees. Armed with sensors and sophisticated feedback equipment, cobots respond to changes in the workflow and help their human partners perform tasks accurately and safely. Some experts predict that the cobot market (currently valued at $1.1 billion) will expand to $9.2 million by 2028).
Performing Tedious and Dangerous Tasks
Robots can also complete tasks that are too tedious for humans, such as inspecting pipelines or sorting items. Additionally, they can monitor and analyze data in real time, allowing workers to make better informed decisions. In the oil and gas industry, for instance, robots inspect pipelines and inspect wells.
And it is not just repetitive and boring tasks, either. That is, another argument in favor of robots in the workplace is that they can perform hazardous tasks, such as working in extreme temperatures and dangerous environments; and cleaning up harmful materials.
One of of the most recently developed robots who might be fit for these tasks is MARVEL, appropriately named because of its superhero abilities. MARVEL is an acronym for Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion.
The brainchild of a research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), this robot is equipped with magnetic foot pads that can be turned on or off.
With these specialized feet, MARVEL can rapidly climb steel walls and ceilings, at speeds of 50 cm to 70 cm a second. Its design and speed make it appropriate for several tricky tasks requiring nimbleness, such as performing inspections and maintenance on high structures (bridges, buildings, ships, and transmission towers.)
Imagine, for a second, MARVEL safely performing maintenance on the Houghton lift bridge while it is still operational. No need to block off one lane and slow down the flow of traffic. No need to be late for work!
Taking Our Jobs? Maybe.
We are approaching a time when machines will be able to outperform humans at almost any task. I believe that society needs to confront this question before it is upon us: if machines are capable of doing almost any work humans can do, what will humans do?
One of the most obvious downsides to incorporating robots in the workplace is that they will lead to job losses. That is, some experts estimate that as many as 20 million job losses will result as companies continue to rely on automation.
Critiquing Robots and Automation
Futurist and New York Times best-selling author Martin Ford has probably been the most vocal about the negative economic and social impacts of automation and robotics.
He has written Rule of the Robots: How Artificial Intelligence will Transform Everything (2021), Architects of Intelligence: The Truth About AI and the People Building it (2018), and Rise of the Robots: Technology and the Threat of a Jobless Future (2015).
Ford has argued that automation and robotics will result in job losses, wage stagnation, and widening inequality. These effects, which will be felt most acutely by low-skilled and middle-skilled workers, will also weaken worker bargaining power.

Alleviating These Problems
But there are solutions. That is, Ford has advocated that governments should prepare for and then take steps to address the issues posed by robotics and automation. Governing bodies could provide better access to education and new job training, invest in infrastructure, promote job-sharing, and provide more generous unemployment benefits.
To alleviate inequities caused by increasing automation, Ford has urged governments to create tax incentives that encourage employers to hire people and train them in the use of robots; or for companies to invest in robots designed to complement rather than replace human workers (such as cobots). He has also supported a basic monthly income for citizens so that everyone has a decent standard of living. How will this monthly income be funded? By taxing companies that use robots, or taxing the robots themselves to generate this income.
MIT professors Erik Brynjolfsson and Andrew McAfee, who wrote The Second Machine Age: Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies, also summarized the second machine age and evaluated in terms of its positive benefits (“bounty”) and increasing inequality (“spread”). After stating that the spread of technology is causing greater inequality, they proposed some similar policy interventions.
Defending Robots in the Workplace
Critics of Ford, McAfee, and Brynjolfsson, such as economists Lawrence Summers and Robert Gordon, and industry expert Jeff Bezos, take a contradictory perspective. They argue that robots and automation will create more jobs than they destroy. These technologies, they contend, will also lead to advanced productivity and efficiency, improved demands for goods and services, and, therefore, increased employment. Robots can also help reduce costs, which could lead to increased profits for companies and more jobs overall.
Summers takes a slightly different stand, affirming that robots could increase production and therefore benefit the economy and improve employment. However, governments should still invest in education and job training to ensure that workers have the skills needed to take advantage of the opportunities created by both automation and robotics.
Futurists at the Information Technology and Innovation Foundation (ITIF) have sung the praises of robots and automation for years. Their experts content that robots and automation will enhance productivity and reshape global supply chains. New production systems, they claim, will bring more (not less) manufacturing work to the United States.
And then there are the numbers, which currently don’t look that fearful. According to the International Federation of Robotics, in the United States, there were only 255 robotic units per 10,000 employees. Although 47% of CEOs are investing in robots (according to a poll by Forbes, Xometry, and Zogby), robots still only have a 2% presence in industry.
Whatever the industry, it is obvious that robots can increase both efficiency and safety. They can work 24/7. They won’t tire during a 16-hour shift, get repetitive stress injuries, or have fatigue-related workplace accidents. Robots can also increase output capacity by helping American manufacturers save on utilities and worker resources, so that they can compete more effectively with offshore companies.
Preparing for an Automated and Robotic Future

This blog has just scratched the surface of robots in the workplace. That is, it didn’t discuss robotic doctors, such as the impressive Davinci Surgical System. Also, the writer doesn’t pretend to be an expert here, just an ex Sci-Fi teacher fascinated with the robotic present and future.
Those who want to prepare for a future in robotics and automation can learn more by taking several educational paths at Michigan Tech. MTU offers major and minor degrees in computer engineering, data acquisition and industrial control, electrical and computer engineering, mechanical engineering, and robotics engineering.
More specifically, there is mechatronics: a field of engineering that combines mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering to create systems that can interact with the physical world. Mechatronic systems consist of sensors, actuators, and control systems. These systems are fundamental to creating robots and other automated systems. Students in this program can also join the Robotics Systems Enterprise “to solve real-world engineering problems.”
Through Global Campus, Michigan Tech also offers several related online graduate certificates in artificial intelligence in healthcare, manufacturing engineering, the safety and security of autonomous cyber-physical systems, and security and privacy in healthcare. It also offers an Online Foundations of Cybersecurity Certificate.
And if you’re interesting in earning an online master’s degree, please check out our MS in Electrical and Computer Engineering or our online Mechanical Engineering programs, both MS and PhD.



