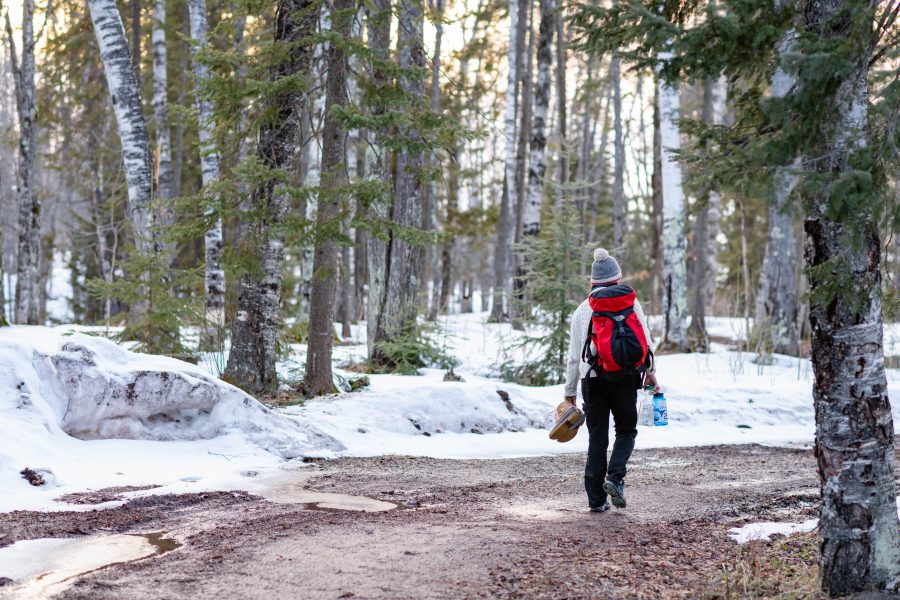
Psychological research is advancing our understanding of how time in nature can improve our mental health and sharpen our cognition. From a stroll through a city park to a day spent hiking in the wilderness, exposure to nature has been linked to a host of benefits, including improved attention, lower stress, better mood, improved immune system, reduced risk of psychiatric disorders and even upticks in empathy and cooperation. [Source: https://www.apa.org/monitor/2020/04/nurtured-nature]
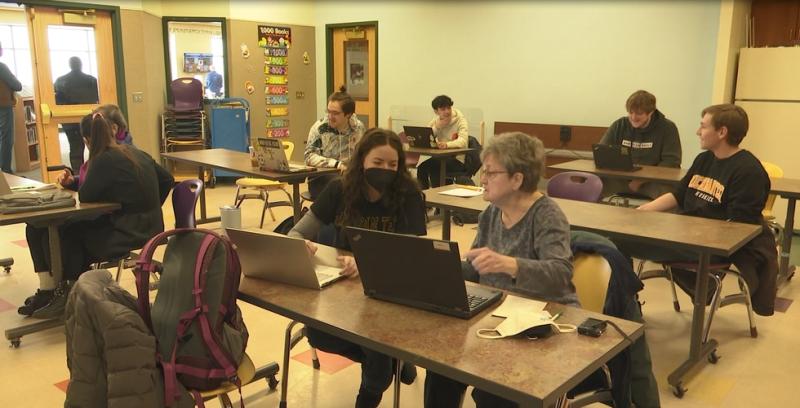
The Department of Cognitive and Learning Sciences has blended these wellness findings with the area’s abundance of outdoor activities and endless beauty into its new course – Nature Psychology. The course was developed by Dr. Samantha Smith, CLS assistant professor, with noteworthy contributions from several other faculty at MTU.The new course centers experiential learning and takes an innovative and interdisciplinary approach to helping students explore how our mental experience is connected to the natural environment.
The course also featured a significant service learning component. In collaboration with Jill Fisher, program manager at the Keweenaw Land Trust (KLT), the students designed a pamphlet explaining many ways that spending time in nature is good for mental health, physical health, and cognitive performance. The pamphlet will be placed at various KLT trailheads and around the local community. The class also created a family-oriented activity with the aim of getting more people exploring the great outdoors, and the KLT-protected lands in particular.
This year’s course culminated with a weekend nature retreat in the Porcupine Mountains Wilderness State Park, allowing students to directly experience and reflect on concepts they discussed throughout the semester. The retreat, facilitated by Dr. Smith and Dr. Erika Vye, included hiking, outdoor cooking, nature-themed discussions and crafts, and time for interpersonal connection and reflection.
Complementary Research and Curriculum Development
In addition to learning about traditional psychology themes, like the impact of time in nature on cognitive performance and mental health, the new course introduced students to a variety of other perspectives on the human-nature connection. Brigitte Morin (BioSci) illuminated the human body’s physiological response to spending mindful time in the natural world, and Dr. Mark Rhodes (SS) led students on an exploration of human geography, political ecology, and what the word “nature” really means. Dr. Chelsea Schelly (SS) engaged students in an exciting examination of environmentally responsible behaviors, and our interdependent relationship with the biophysical world from a sociological lens. Lisa Gordillo (VPA) spoke to some of her own and others’ work at the intersection of art and ecology to facilitate community engagement and conversations about environmental justice and human rights. Dr. Erika Vye (GLRC) introduced students to the importance of varied personal values for geologic features, the wide-ranging connections people have with landscape, and the value of geoheritage as a geoscience communication tool affording place-based learning experiences that nurture our sense of place. Dr. R.J. Laverne (CFRES) shared his expertise on urban forestry, and the consequences of becoming too disconnected from the natural world that we evolved to thrive in.
The takeaways to keep for life
Throughout the course, students gained a greater understanding of:
- how nature impacts human psychology and physiology,
- how an understanding of psychology and the human-nature connection can be used to promote positive social and environmental outcomes,
- how to engage in and promote environmental stewardship efforts and become more environmentally responsible citizens of the Earth.
There’s More
The Nature Psychology course is not the only experiential learning opportunity provided by the CLS department. Course offerings also include Environmental Psychology, where students go outside the classroom to observe psychological principles and practices at play in various real-world settings. For example, during the course, students conduct a walkability survey of Houghton, and conduct a scavenger hunt at the A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum to explore the design of educational environments.
In the fall semester, during the Upper Peninsula’s famous “color season”, the department also organizes a “Psych Hike” – a group hike on one of the area’s beautiful trails. This is a great way to calm the mind, move the body, and enjoy time together in nature.
For more information regarding our Psychology and Human Factors programs, please contact us at cls@mtu.edu. And for the latest happenings, follow us on Instagram @clsmtu or Facebook
Photo credit: Hannah DeRuyter