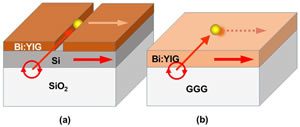
 Miguel Levy (Physics/MSE) and Dolendra Karki (Physics) authored a paper published this month in Scientific Reports — Nature, entitled “Nonreciprocal Transverse Photonic Spin and Magnetization-Induced Electromagnetic Spin-Orbit Coupling.”
Miguel Levy (Physics/MSE) and Dolendra Karki (Physics) authored a paper published this month in Scientific Reports — Nature, entitled “Nonreciprocal Transverse Photonic Spin and Magnetization-Induced Electromagnetic Spin-Orbit Coupling.”
doi:10.1038/srep39972