Camping. Sounds like a cliché, but it was through this humble activity that Rick Berkey first discovered Michigan’s Upper Peninsula.
These trips inspired a love for the area that caused him to eventually wend his way to Michigan Tech.
That is, Berkey and his soon-to-be wife, Tiffany, had been regularly visiting the UP for three years.
But it was their trip to Copper Harbor in 2002 on their one-year anniversary that sealed the deal.
The natural beauty, outdoor activities, down-to-earth people, and peaceful, small-town life were all reasons they fell in love with the Keweenaw. Here, in their eyes, was the ideal place to raise a family. And even better: Rick was ready for a career change.
So, together, they started hatching a plan to relocate to the beautiful UP.
That plan finally came to fruition in 2006 when Rick accepted a position in the College of Engineering working with the Enterprise and Senior Design programs. With a two-year old daughter, two month-old son, dog, and cat all in tow, they made the 550-mile journey from Kalamazoo to Houghton, closed on their new house, and slept on the floor that night.
Sitting Down With Rick Berkey
A few career moves later, Rick is bringing his enthusiasm, expertise, and love of Michigan Tech to a new leadership role at Global Campus. Even though he is a busy man, he graciously took time out of his day to answer my questions.
Hello, thank you for agreeing to this interview. First, please state your title and your position at Global Campus. I know you’re a new team member, but so far, what duties comprise your role?
My title is “Director of Global Campus and Continuing Education.”
In this role, I am responsible for the overall operations of Global Campus as it continues to grow and expand. These operations include staff and financial management, as well as collaboration with colleges and departments to oversee our portfolio of online degrees, certificates, and non-credit programs.
You previously served as Professor of Practice and Director of the Enterprise Program. Please tell us a little more about these roles and how they will help you in your new position at Global Campus.
In my previous appointment as a Professor of Practice, I thoroughly enjoyed teaching undergraduate students in the Enterprise Program. In this role, I developed and taught two courses in Six Sigma/continuous improvement methodologies. These courses were inspired by my corporate experience as a Six Sigma Black Belt. I also advised the Supermileage Systems Enterprise, a competition team that developed highly-efficient vehicles from the ground up.
These roles taught me to embrace experiential, hands-on, discovery-based learning, which can be time-intensive, messy, and sometimes uncomfortable. To me, though, these are all signs that the learning is working! Similarly, my teaching philosophy is based on learning as a partnership and creating an environment where everyone contributes to learning. One quote that really resonates with me is this one from Robert A. Heinlein: “When one teaches, two learn.”
My teaching experience definitely provides a valuable perspective when working with the faculty who are developing and delivering our online and non-credit programs. That is, I both understand and appreciate the challenges associated with course development, delivery, and assessment. Additionally, I have the opportunity to continue teaching in Global Campus. When I do so, I will be refreshing and adapting my Six Sigma courses for online/non-credit audiences.
As Director of the Enterprise Program (2015-2022), for example, I managed the operations of Michigan Tech’s signature experiential learning program: Enterprise. This program included industry partnerships, project development, financial and staff management, course scheduling, and event planning. It also entailed collaborating with 25+ faculty from across campus and assessing student learning outcomes for ABET accreditation. Again, this experience translates well into managing the operations of Global Campus.
You hold a Six Sigma Black Belt. Wow! Tell us a little more about this certifications, how/when you earned it.
Earning my Six Sigma Black Belt certification through Honeywell International was a career-changing experience. The training was intense and involved use of structured, data-driven problem-solving methods and statistical tools. It also included training in change management, which is often more important than what the data and statistics are telling you. My favorite part of the experience was applying my learning to the development and launch of the FRAM X2 Extended Guard oil filter product line. That is, I really enjoyed using statistics to develop our competitive performance claims. This task was important because these claims were advertised on the product packaging. Thus, these claims could be challenged legally by our competitors. So no pressure if I didn’t get it right!
I also used design of experiments (DOE) to optimize a new supplier’s manufacturing process, which was critical to both product performance and cost. At this moment, I am now reminded of the DOE I had to re-run because I missed an important factor in the process. After a 16-hour day, we discovered our test samples were defective and had to do it all over again. Our Director of Engineering was, shall I say, not happy.
Talk about learning from failure! I draw on this experience even now, and especially when teaching. Another favorite experience was teaching and mentoring our Six Sigma Green Belt candidates. In fact, this is ultimately what motivated me to transition from the corporate world to higher education.
I really believe that FAIL should be viewed as “First Attempt In Learning.”
And you are certified in Lean, as well, correct?
Yes! Fast forward 11 years later…not too long after I came to Michigan Tech, I “found my people” in the Office of Continuous Improvement. Those in the office were applying Lean to improve university processes. I quickly got involved with Lean Culture though several campus improvement projects and jumped at the chance to become a Lean Facilitator. Adding a certification in Lean has provided me with a complementary tool set to the more analytical, data-driven methods used in Six Sigma.
A favorite Lean experience of mine was working with Accounting Services on the “P-Card Kaizen.” We were able to streamline accounting processes by shifting purchases from purchase orders to p-cards. I especially enjoyed using control charts in Minitab to reveal before vs. after results. We also showed how the staff time saved could be redirected to higher-value work and tasks.
Overall, my exposure to the Lean and Six Sigma methodologies has really shaped how I approach work and life: systematic, data-driven, analytical, and improvement-minded.
Why get involved with online graduate education and online professional development programs? That is, why do YOU think online education matters?
Looking back on my own experience, I was a non-traditional student twice. The first time, I was taking night classes for my MBA. Then, I was working full-time for Honeywell and establishing my professional career. The second time, I was here at MTU earning my MSME while doing all the things I mentioned earlier. In both cases, I felt the college experience was designed for full-time students, not me.
Although I was fortunate to have work flexibility to attend classes, it was still challenging to balance school and life. At the same time, I had a much stronger sense of why I wanted to learn something new. I also had more life experience to draw upon and to contribute in the classroom. And I know there are many more people out there in similar situations and who are motivated to continue learning and growing.
When I look at the flexibility that Global Campus offers, coupled with the quality and reputation of Michigan Tech’s programs, I knew this was where I wanted to make an impact.
So far, what has been the most rewarding and/or exciting part of your job? In other words, what gets you out of bed in the morning?
Tough question! There are so many exciting and rewarding elements for me in these first few months on the job! Global Campus is still relatively new and very dynamic. In many ways, it feels like a start-up that requires us to wear many hats and adopt an entrepreneurial mindset.
That said, two things in particular help get me out of bed every morning. First, I find all the work we do with our education fellowships extremely rewarding. Whether it’s holding informational sessions, meeting with partners to explore their educational needs and interests, or assisting corporate employees enrolled in our programs, I am committed to serving our partners and helping them achieve their higher education goals. Secondly, I get excited about improving our processes and operations as we grow.
Recently, I’ve been doing a lot of listening and learning to establish a solid baseline of what we do and how we do it. I am now starting to identify some areas where we can streamline and scale how we operate, while maintaining or improving our quality and service. This improvement will ultimately allow us to serve more students and increase the impact and reach of Global Campus.
When you’re not working for Campus, what do you like to do in your free time? Where might we find Rick Berkey after work or on the weekend?
Outside of work, my family and I, like another Global Campus team member, really enjoy the outdoors. In particular, we love camping, boating, hiking, and nordic skiing. The great thing is that we can do all of these things after work or on the weekend. Copper Harbor is a favorite local destination. We also like to travel, and when we need to get our “second wind” during the long winters, we tend to go south to a sandy beach! With our families living 500+ miles away downstate and in Ohio, we also make time, of course, to visit them during holidays and summer vacations.
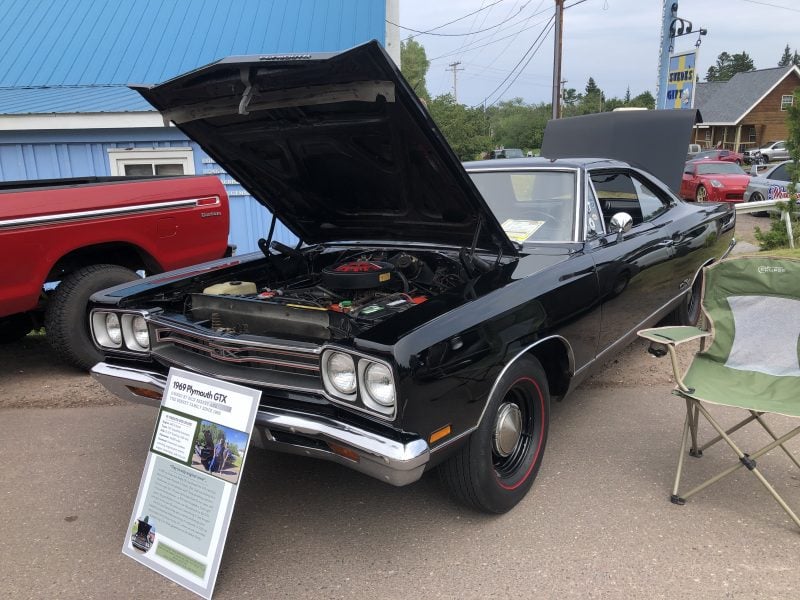
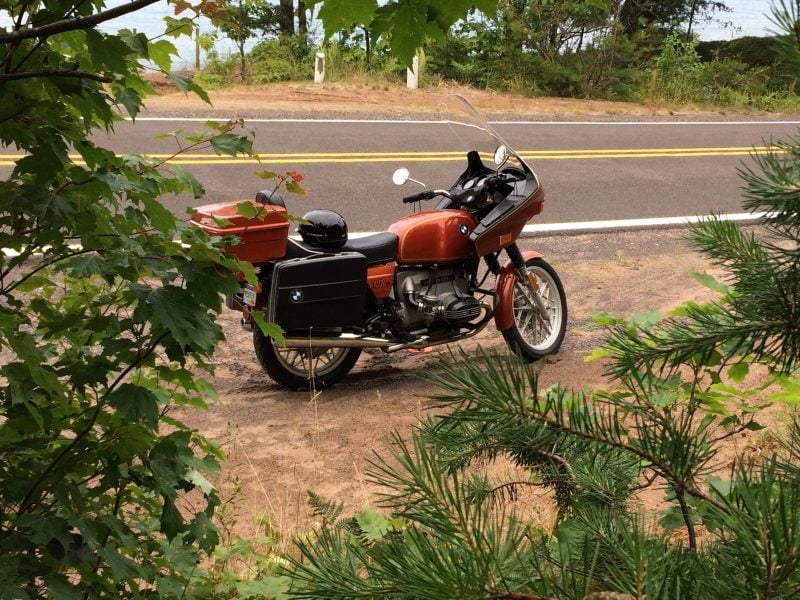
In addition to family activities, I personally enjoy classic vehicles: cars, motorcycles, boats, campers…you name it. I must be an “old soul”. In particular, I really enjoy researching the history of vehicles, doing restoration and maintenance, socializing with fellow collectors and enthusiasts, and especially searching for a new “investment,” as I tell my wife!
Currently, I own three classic motorcycles as well as our family’s pride and joy: an all-original 1969 Plymouth GTX that was purchased new by my father. It’s an heirloom that will remain in the Berkey family for future generations.
Keeping Up With the New Director of Global Campus
Thanks for chatting! Readers, be sure to follow Rick Berkey and his exploits on Global Campus social media.