Coming in Fall 2024, the College of Forest Resources and Environmental Science (CFRES) will be offering a new online graduate certificate: Foundations in Geographic Information Science (GIScience) for Natural Resources. Taught by Dr. Parth Bhatt, Associate Teaching Professor / Researcher at CFRES, this certificate consists of three foundational courses. They are GIS for Natural Resource Management (4 credits), Map Design With GIS (3 credits), and GPS Field Techniques (2 credits).
This certificate is the first of three that will form CFRES’s new online master’s degree in GIScience (currently under development). The others will be Advanced Geographic Information Science for Natural Resources and Remote Sensing for Natural Resources. These two will comprise rigorous courses in Python, Applied Spatial Statistics, GIS Project Management, Advanced Terrestrial Remote Sensing, Photogrammetry, and more. In other words, this online MS degree will equip graduates with a rich, varied skill set in GIScience. They will also acquire a holistic, deep understanding of the spatial dimensions of the world.
For a decade, CFRES has offered a respected, in-person MGIS. Like its predecessor, this interdisciplinary online master’s degree will emphasize practical skills in spatial visualization and analysis. Students will use real-world datasets and state-of-the-art GIS software and techniques to take on challenges in forestry, natural resources, and other disciplines.
The reputation of CFRES, the program’s emphasis on natural resources, and its robust curriculum promise to make this program a highly esteemed online GIS master’s degree. Global Campus is thrilled to be involved with it!
Applying GIScience in Forestry and Natural Resources
If you’re not familiar with Geographic Information Science, it is an exciting, growing, multidisciplinary field. It focuses on the study of geographic information, spatial data, as well as their applications. Combining principles from geography, computer science, mathematics, and other disciplines, GIScience has the ambitious goal of understanding, analyzing, and modelling the spatial aspects of the world.
GIS, or Geographical Information Systems, focuses on the what: the hardware and software that capture geographic information. In contrast, GIScience, focuses on the why: finding practical ways to improve GIS data, software, and professional practice.
This certificate and upcoming MGIS will provide fundamental GIScience expertise to foresters and natural resource experts. In Natural Resource Management, for example, professionals use GIScience for several purposes:
- resource inventory and mapping
- environmental impact assessment
- habitat modeling and conservation planning
- natural disaster management
- sustainable land use planning

Take resource inventory and mapping. Natural resource managers turn to GIScience to create detailed inventories and maps of natural resources. This data then allows them to analyze the distribution and abundance of resources within an area: forest stands, wetlands, mineral deposits, endangered species habitats, and other important ecological features.
Alternatively, in habitat modeling and conservation planning, experts use GIScience tools to analyze the suitability of habitats for different species. This suitability is based on environmental variables such as temperature, precipitation, elevation, and vegetation cover. GIScience, in short, is crucial to conservation planning. It can help identify critical habitats, corridors for wildlife movement, and areas for habitat restoration or protection.
Solving Multiple Problems With GIScience
First and foremost, GIScience offers practical skills and tools for professionals in several natural resource fields. These include GIS Analysts/Technicians, foresters, civil and environmental engineers, spatial/transportation planners, wildlife ecologists, forest analysts, surveyors, geospatial specialists, water resources analysts, environmental scientists, geologists, community forest specialists, and urban forestry technicians.
Several, in fact, turn to this toolkit regularly. One previous alum from the in-person MGIS now works as a Senior GIS Analyst. In this role for Pine Gate Renewables, he uses GIS and Remote Sensing daily. These tools help him to identify risks for setting up solar farms, creating hydrology models, and locating wetlands.
Another alum with broad responsibilities also confirmed the daily use of GIScience. He oversees the creation of maps, spatial data analysis, surveying projects, data checks on road segments, and storm water analysis “to create pervious and impervious classification.” This person also admits to “diligently maintaining maps detailing water infrastructure” and managing and reviewing “various city assets, ensuring their accuracy and reliability through spatial data analysis.”
In other words, these alumni regularly manage several responsibilities with GIScience and Remote Sensing.
Contending With Climate Change
Regardless of their discipline, GIScience can also equip professionals with the tools and the strategies to predict and combat the effects of climate change.
This skillset is especially relevant now: 2023 was the warmest year on record. (The temperature was 1.18°C [2.12°F] above the 20th-century average of 13.9°C [57.0°F]. In fact, the last ten warmest years in the 174-year record have all occurred between 2014 and 2023. And with a heating planet come more impactful environmental events: floods, extreme weather, drought, and forest fires.
According to NOAA, 2023 also set another record–for natural disasters. During this year, there were 28 devastating weather and climate disasters. The price tag for these events was almost 93 billon dollars.
For contending with climate change’s effects, then, GIScience can aid with hazard mapping, risk assessment, and emergency response planning. For instance, by analyzing spatial data related to factors such as terrain, vegetation, hydrology, and population density, professionals can identify areas prone to natural hazards. Whether these are floods, wildfires, and landslides, experts can develop strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively during emergencies.
The Pakistan Flood Events
Dr. Parth Bhatt, himself, used GI Science to document the effects of Pakistan’s historic floods, which lasted from June 15 to October 2022.
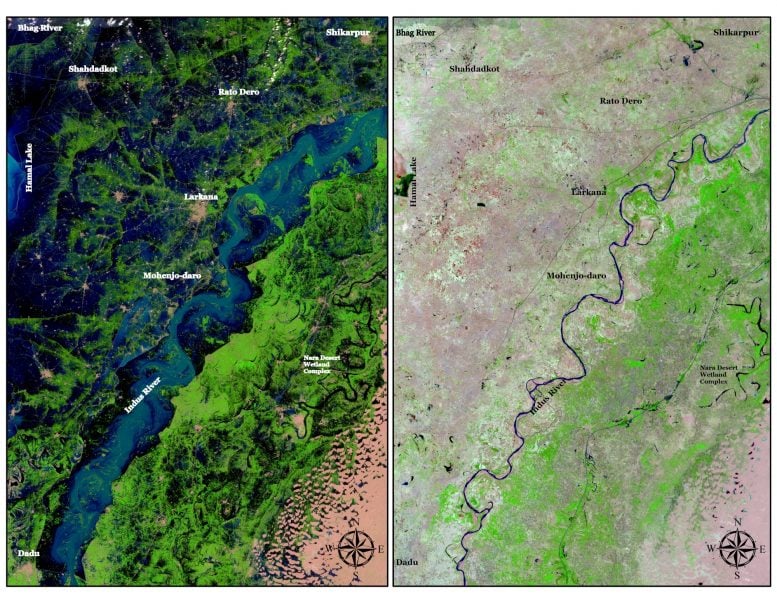
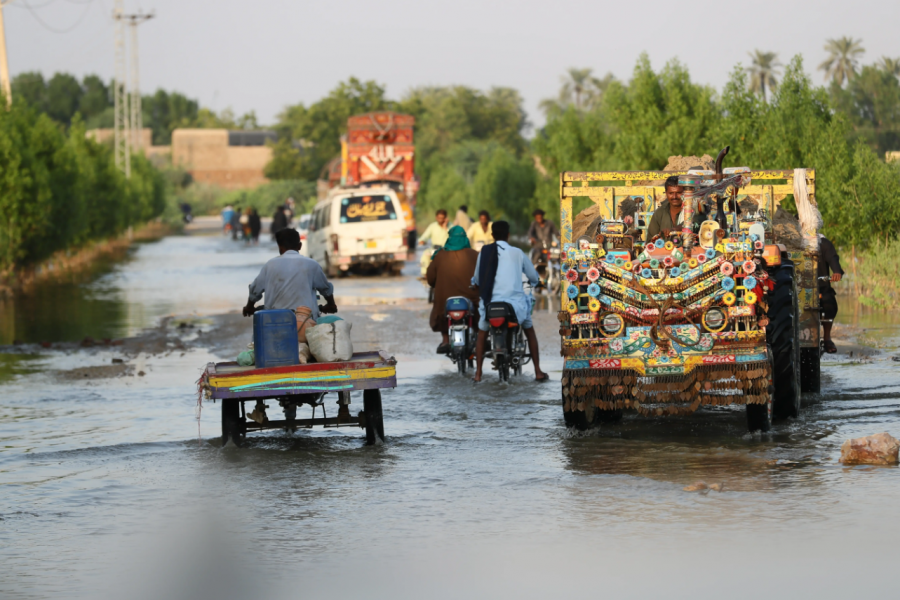


In these devastating flood events, waters inundated more than one million homes. The flood hit all four of the country’s provinces, resulting in at least two million houses destroyed.
In total, 33 million people were directly affected with 20.6 million requiring urgent humanitarian assistance. (Unfortunately, nine months later, the monsoons brought more flooding, further exacerbating the crisis.)
Looking Ahead to the Future of GIScience
GIScience, in short, can help professionals in many fields manage the world’s resources, plan infrastructure, mitigate and plan for natural hazards, and combat (or prepare for) the effects of climate change, and more.
However, its tools are also becoming increasingly integral in fields beyond traditional domains like urban planning and environmental science.
As GIScience “continues to evolve and adapt to new demands, its impact on industries and disciplines worldwide is set to expand. As such, it will drive “transformative change and unlocking new possibilities for spatial analysis and decision-making” (GIS Analyst II). For instance, some of the newer industries hiring GIS experts are construction, engineering, insurance, real estate, and oil and gas.
One Senior GIS Specialist (Pine Gate Renewables) further confirmed that in the solar industry, there are more people being hired with a GIScience background than there were before. More professionals use “GIS and remote sensing to help identify issues, notice change over time, help drive decisions, and keep projects moving forward.”
Another expert stated that proficiencies in ArcGIS, QGIS, Python, R, and Javscript are becoming increasingly essential in GIS specialist roles.
From agriculture to healthcare, smart cities to disaster management, GIS and Remote Sensing are revolutionizing how we analyze spatial data, make informed decisions, and address complex challenges. Integration with emerging technologies like AI, along with a focus on environmental monitoring, public health, and conservation, underscores their pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable and interconnected world.
Learning From a Passionate Teacher
And it’s not just what you will learn in these programs but who you will learn it from. That is, Foundations in GI Science for Natural Resources (and the online MGIS) are both helmed and taught by Dr. Parth Bhatt, whose passion for the subject was covered in a previous blog.
Bhatt’s portfolio of GIScience skills is also diverse: he has expertise in Geographical Information Systems, remote sensing, digital image processing (Multispectral, LiDAR, UAV, Hyperspectral), land use/cover mapping, invasive species mapping, forest health and natural resource management, spatial data analysis, and Web GIS/ArcGIS Online.
Most recently, he has received a grant to put these skills to work: acting as a PI on research projects for The Nature Conservancy in Michigan.

Bhatt has also been instructing the very popular, noncredit, professional development course, Python for Modern GIS and Remote Sensing. This course, which runs several times a year, has had rave reviews.
Taking the Next Steps
If you’d like to learn more about GIScience or you require more information about the Online GIS Certificate from CFRES, please contact Program Director Parth Bhatt (ppbhatt@mtu.edu).
Alternatively, reach out to Program Assistant Marjorie Banovetz (marjorie@mtu.edu).
There is still plenty of time to get started for Fall 2024 and develop your versatile GIS toolkit! And accelerated options are also available.