The miners in the boom days of the Copper Country knew that in order to find what they wanted, they had to “drill down.” Today, thanks to the efforts of researchers in Michigan Technological University’s Social Sciences Department and a grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities, those wishing to find out about the people and the places of the Keweenaw’s past can “drill down” through history.
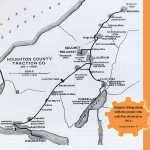
Keweenaw Time Traveler is an online map-based tool allowing visitors to explore the layers of history for any location in the Houghton, Keweenaw and Ontonagon county region. The project uses proven technologies and techniques of participatory Geographic Information Systems (GIS). It also employs collections of geographic data and tools that are interactively connected, enabling users to incorporate their own information about a place and store that data long-term, to create a high-resolution database that maps changes in the social, natural, industrial and built environments of the Copper Country from 1850 to 1970.
The project is the brainchild of Social Sciences faculty Don Lafreniere, assistant professor of historical geography; Sarah Scarlett, assistant professor of history; and PhD candidate John Arnold, an architect by profession. They have received $259,882 from the National Endowment of the Humanities to support their work.
The project can be accessed at http://www.keweenawhistory.com.
Read the full story.
From Tech Today.