
Mechanical Engineering–Engineering Mechanics
The verification and validation (V&V) process for a typical automotive vehicle and powertrain electronic control unit takes approximately two years, and costs several million dollars. V&V are essential stages in the design cycle of an industrial controller, there to remove any gap between the designed and implemented controller. Computer modeling has brought about improvements over the years, but the gap remains.
Michigan Tech researcher Mahdi Shahbakhti has made significant progress to remove that gap, using system models to easily verify controller design. His solution features an adaptive sliding mode controller (SMC) that helps the controller deal with imprecisions in the implementation of the system.
The research is funded by the National Science Foundation GOALI program, or Grant Opportunities for Academic Liaison with Industry. Shahbakhti’s team and fellow researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, and Toyota USA in Ann Arbor, Michigan are nearing the end of their three-year collaborative GOALI project.
“Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is one of the main sources of controller implementation imprecisions, mostly due to sampling and quantization,” says Shahbakhti. “Our approach mitigates ADC imprecisions by first identifying them in the early stages of the controller design cycle. We first developed a mechanism for real-time prediction of uncertainties due to ADC and then determined how those uncertainties propagated through the controller. Finally we incorporated those predicted uncertainties into the discrete sliding mode controller (DSMC) design.”
“Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is one of the main sources of controller implementation imprecisions, mostly due to sampling and quantization.”
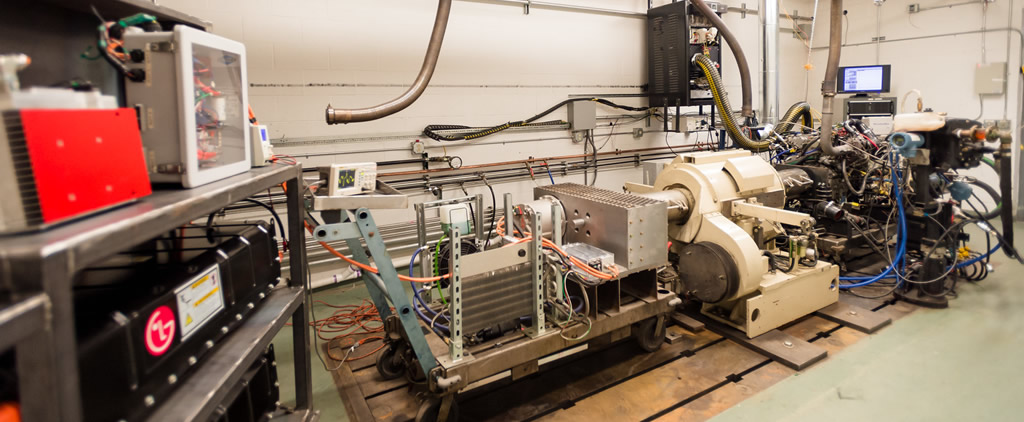
Shahbakhti and his team tested an actual electronic control unit at Michigan Tech in a real time processor-in-the-loop setup. Their approach significantly improved controller robustness to ADC imprecisions when compared to a baseline sliding controller. In a case study controlling the engine speed and air-fuel ratio of a spark ignition engine, the DSMC design with predicted uncertainty provided a 93 percent improvement compared to a baseline sliding controller.
Toyota works closely with the research team to integrate GOALI project results into the design cycle for its automotive controllers. The company provided team members with an initial week of training on its V&V method of industrial controllers, and also participates with Shabakhti’s team in online biweekly meetings. “The concept of this project is fundamental and generic—it can be applied to any control system, but complex systems, such as those in automotive applications, will benefit most,” notes Shahbakhti.

