
Bruce Lee will share his knowledge on Husky Bites, a free, interactive Zoom webinar on Monday, 3/20 at 6 pm ET. Learn something new in just 30 minutes or so, with time after for Q&A! Get the full scoop and register at mtu.edu/huskybites.
What are you doing for supper this Monday 3/20 at 6 p.m. ET? Grab a bite with Dean Janet Callahan and Bruce Lee, professor of Biomedical Engineering at Michigan Tech.
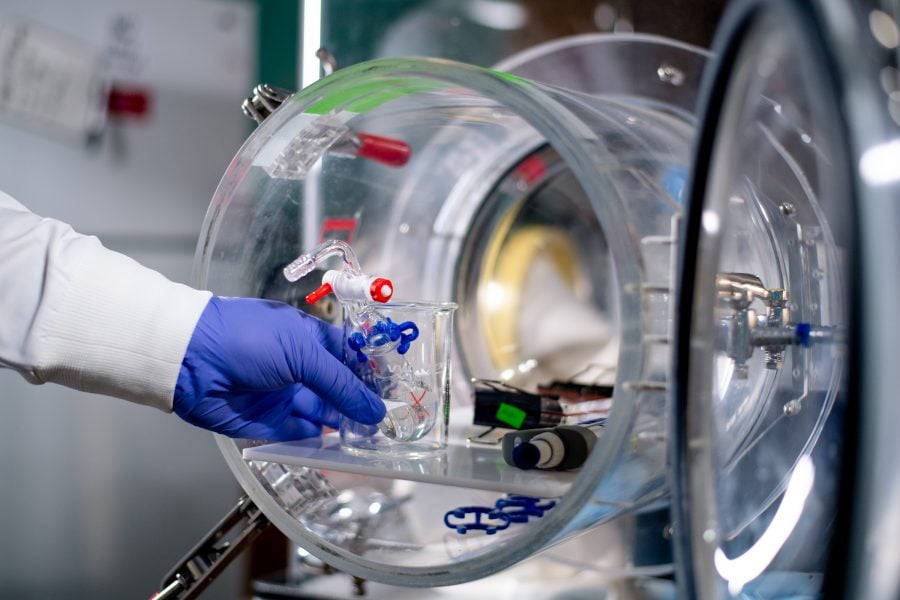
A smart adhesive doesn’t need to adhere all the time. Prof. Bruce Lee looks to biological sources to develop adhesives that can be turned on and off. During Husky Bites, he’ll talk about his work with these advanced adhesives, and their origin: mussel foot proteins. One of those proteins is DOPA (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine). DOPA helps mussels cling to their underwater homes. Lee also uses catechols, synthetic compounds that mimic the wet-but-still-sticky proteins secreted by mussels.

Joining in will be biomedical engineering PhD student Fatemeh Razaviamri. She’s a member of Dr. Lee’s research group. Her research on moisture-activated antiviral coating based on mussel adhesive chemistry earned First Prize for Oral Presentation at the Michigan Tech 2022 Graduate Research Colloquium.
With a small zap of electricity, Lee and his research team can take an underwater smart glue prototype from sticky to not in seven seconds.

“It’s one thing to do this in the open air and quite another under water,” Lee says.
The technology could help with wound dressings, prosthetic attachments or even making car parts and in other manufacturing.
“A lot of people have been using catechol to mimic mussels and their adhesive proteins, but applying electricity to deactivate it is new,” Lee adds.
“Applying electricity is convenient. It can be potentially integrated with electronic devices. Detaching a smart glue with electricity could also be automated and could be as simple as pushing a button.”
Dr. Lee recently found that the adhesive he is developing generates hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct. “Hydrogen peroxide is a mild reactive oxygen species and is a signaling molecule that is critical to normal wound healing process,” he explains. “Hydrogen peroxide is also a natural disinfectant.” Next, he aims to control the release of hydrogen peroxide from his adhesive to promote dermal wound healing in diabetic patients. “This adhesive would have the added benefit in preventing infection.”
Dr. Lee earned his PhD and MS in Biomedical Engineering at Northwestern University. He earned his BS in Chemical Engineering at Cornell University. Prior to joining Michigan Tech, Dr. Lee helped found a start-up company, Nerites Corporation, which aimed at commercializing biomimetic bioadhesive and antifouling technologies. Nerites Corporation was acquired by Kensey Nash Corporation (part of Royal DSM) in 2011.
In 2016, Lee earned a prestigious Young Investigator Program (YIP) award from the Office of Naval Research to explore underwater smart adhesives. In 2019, he received Michigan Tech’s Bhakta Rath Research Award with his PhD student Ameya Narkar.

Prof. Lee, how did you first get into engineering? What sparked your interest?
I am interested in building things. In graduate school I learned to do chemistry. This is what has enabled me to synthesize various types of polymers for designing functional biomaterials and adhesives. Much of my research centers around our ability to synthesize functional adhesives, as well as specialized adhesive polymers that answer specific scientific questions.
Hometown, family?
I was born in Taipei, Taiwan. I currently live in Houghton with my wife and two sons. Both my sons go to the local middle and high school in Houghton.
Any hobbies?
My main hobby in winter is to drive my sons to hockey games and watch them play hockey!

Fatemeh, how did you first get into engineering? What sparked your interest?
I like designing and making things that give me a chance to show my creativity. The fact of being able to design biomaterials to be used for the well-being of mankind sounds interesting and motivating—and it is.
Hometown, family?
I was born in Sari, Iran. I currently live in Houghton with my husband who is also a PhD student in the Biomedical Engineering department at MTU.
What do you like to do in your spare time?
Swimming, photography, and reading books are my hobbies. I also watch documentaries.
Read more:
Q&A with Bhakta Rath Award Winners Ameya Narkar and Bruce Lee
MTU Engineers Zap and Unstick Underwater Smart Glue

