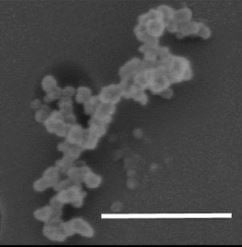
A recent study, Radiative absorption enhancements by black carbon controlled by particle-to-particle heterogeneity in composition, stemming from a collaboration between Brookhaven National Laboratory, Michigan Tech, and other institutions was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) and has been highlighted in the research highlights section of Nature Climate Change this March.
The research resulted in the development of a new modeling approach – guided by experimental results – to account more accurately for the effects of soot on climate. Coauthors of the paper include two former students of the Atmospheric Sciences Ph.D. program from the physics department, Drs. Janarjan Bhandari and Swarup China.
Janarjan Bhadari, ’18, currently works at the Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, and Swarup China, ’14, is at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.