This year’s Three Minute Thesis competition organized by the Graduate Student Government (GSG) of Michigan Tech had great participation both in person at The Orpheum Theater and virtually over Facebook Live. Twenty-eight participants competed at the MUB Ballroom for a place in the finals, held at The Orpheum Theater on Nov. 4.
After a very close competition, Priyanka Kadav, a PhD student from the Department of Chemistry, won first place.
Kadav’s presentation was titled “Capture and Release (CaRe): A novel protein purification technique.” She will go on to represent Michigan Tech at the regional levels of the competition.
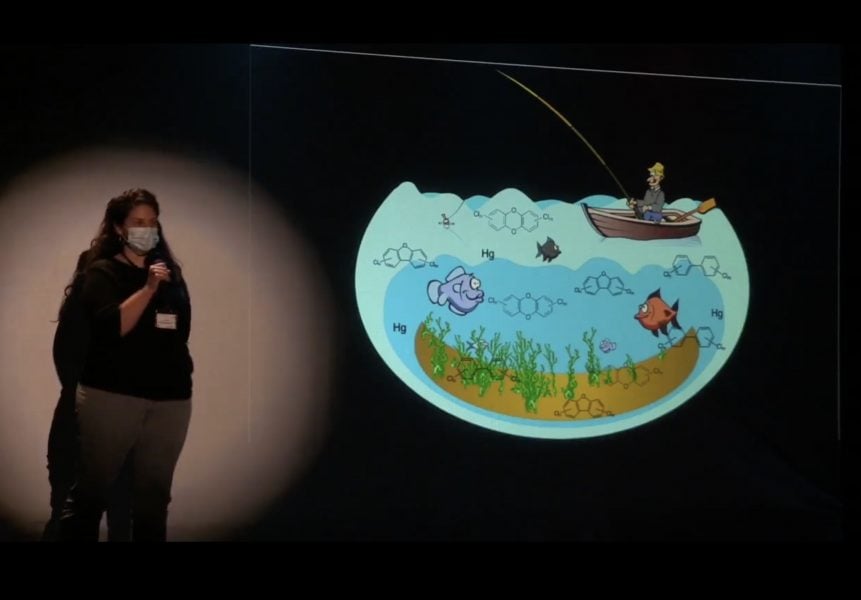
The runner-up was Emily Shaw, a PhD student from the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geospatial Engineering, with a presentation titled “Toxicity in Fish Tissue: Redefining our Understandings by Quantifying Mixture Toxicity.”
Yue (Emily) Kang from the Department of Mathematical Sciences department won the People’s Choice award with her presentation, titled “Robust numerical solvers for flows in fractured porous media.”
Other finalists were:
- Jessica Bruning, Kinesiology and Integrative Physiology
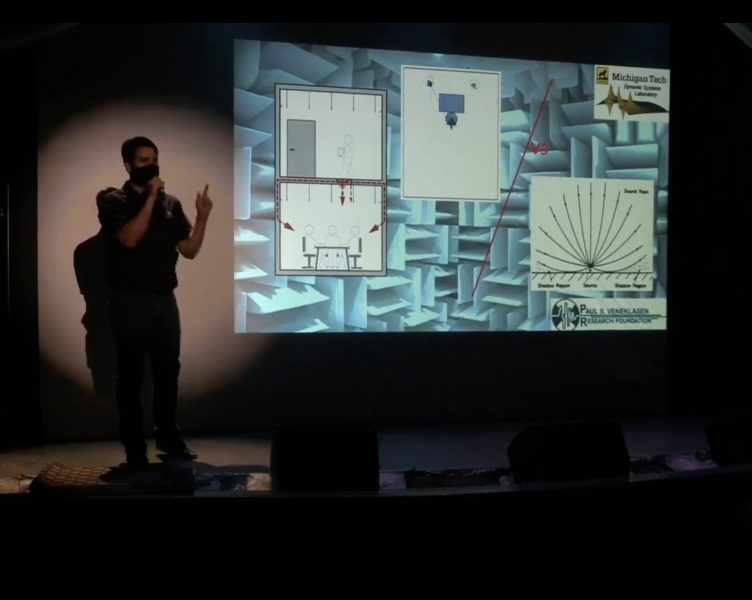
- Sunit Girdhar, Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics, “Reproducible sound measurement method for footstep noise”
- Rob Tunison, College of Forest Resources and Environmental Science
- Arman Tatar, Civil, Environmental, and Geospatial Engineering, “Low-Damage Uplift Friction Dampers for Self-Centering Cross-Laminated Timber Rocking Walls”
- Laura Schaerer, Biological Sciences
- Michael Maurer, Electrical and Computer Engineering, “Integrated Electro-Optic Antennas”
Each presentation was scored by a panel of judges from diverse academic backgrounds. The judges for the finals were:
- Wallace Southerland III, Vice President for Student Affairs and Dean of Students
- Jim Baker, associate vice president for research administration
- Marie Cleveland, a Michigan Tech alumna who was awarded the Alumni Association Outstanding Service Award in 2014
This year’s finals were also streamed live on GSG’s Facebook page and can be watched online.
GSG would also like to thank all the volunteers and The Orpheum Theater for making this event possible.
By Graduate Student Government.