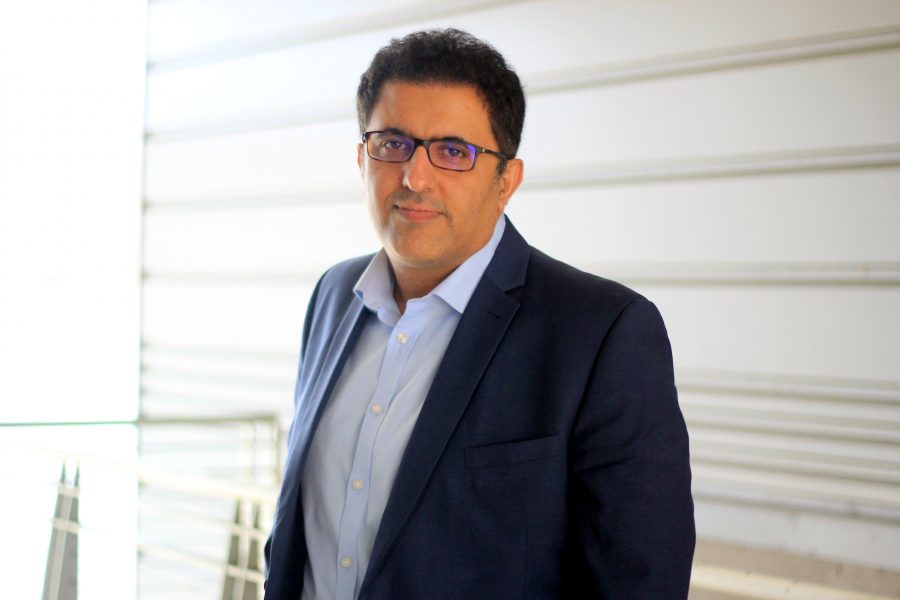
It is with deep sadness that we announce the passing of Professor Emeritus William (Bill) Rose on July 18. A distinguished colleague, devoted mentor, treasured friend, and visionary community leader, Bill began his journey with the Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences (GMES) in 1970, shortly after earning his PhD from Dartmouth College. He dedicated his entire 41-year faculty career to Michigan Tech and the Keweenaw community.
As department chair from 1990 to 1998, Bill led us through transformative growth, expanding graduate programs, increasing external research support, and integrating new technologies into geoscience education and outreach. He was instrumental in establishing signature programs such as the International Masters in Volcanology and Geotechniques (INVOGE) and the Peace Corps Master’s International program in Mitigation of Geologic Natural Hazards—initiatives that have significantly impacted our students and enhanced our global reputation.
Even in retirement, Bill remained deeply engaged, promoting public understanding of geoheritage and sharing his passion for science and culture with the broader community. His generosity, vision, and tireless mentorship have left an indelible mark on all who have had the privilege of knowing him. Many of his students returned decades later to reconnect, a testament to the lasting impact he had on their lives.
Our hearts go out to his wife, Nanno, his sons Christopher and Jason, and their families.
We recognize that no brief message can fully capture his profound impact or enduring legacy. In the coming days, we will share more information and plan a proper tribute to honor Bill’s life and contributions.
Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences