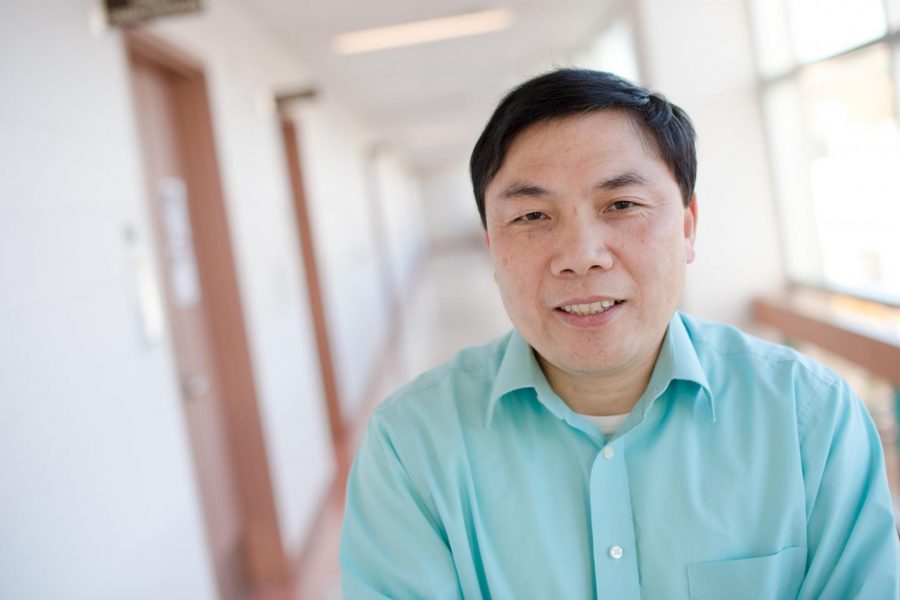
John Jaszczak will share his contagious enthusiasm for minerals on Husky Bites, a free, interactive Zoom webinar on Monday, 3/27 at 6 pm ET. Learn something new in just 30 minutes or so, with time after for Q&A! Get the full scoop and register at mtu.edu/huskybites.

What are you doing for supper this Monday 3/20 at 6 p.m. ET? Grab a bite with Graduate School Dean Will Cantrell and John Jaszczak, Professor of Physics at Michigan Tech. Jaszczak is also the Director and John and Phyllis Seaman Endowed Curator of the A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum. Joining in will be Patrice Cobin, Museum Manager. Cobin is also a Michigan Tech alumna.
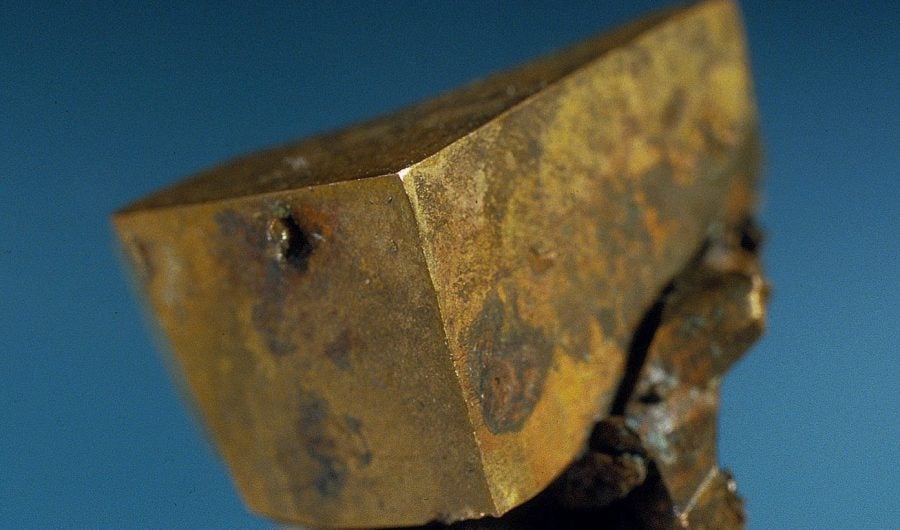
The A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum showcases amazing minerals from the Great Lakes region and around the world. This year is special, as the museum celebrates its 120th anniversary.
The A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum curates approximately 40,000 cataloged objects. The museum houses the world’s finest collection of native copper and other Upper Peninsula minerals, a superb collection of minerals from around the Great Lakes Region, and a broad representation of fine minerals from around the world—all displayed in a 8,000-square-foot building located on the south end of the Michigan Tech campus.

As curator, Jaszczak holds the responsibilities of caring for, growing and utilizing the museum’s collections of minerals and related objects for exhibit, education and research. Mineral collecting is also his long-standing hobby, with over 4,000 specimens in his personal collection.
“Some minerals can have a natural wow factor, and while we use many of them daily without thinking twice, some specimens are truly objects of art,” Jaszczak says.
During Husky Bites, Jaszczak and Cobin will share a little bit of the museum’s long history dating back to the origins of the University in 1885. They’ll share some collection highlights, as well as its mission and current programming.
On April 24, 1990, the Michigan legislature made the A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum the official Mineral Museum of Michigan. With the largest public exhibit of an outstanding collection of minerals from the Great Lakes region, as well, it’s known unofficially as the Great Lakes Mineral Museum, too.
The museum also has a visitor-friendly garden, where rocks of the Great Lakes region are featured. “Most rocks are combinations of one or more minerals,” Cobin explains. “The individual minerals found in rocks can be seen in the exhibit hall.”

Last March, John “Jack” (A. E. Seaman’s grandson) and Phyllis Seaman celebrated Jack’s 103rd birthday with a gift to Michigan Tech. Their endowment ensures the A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum will continue to impact students, scientists and the public for generations to come and provides perpetual support for a museum curator. Prof. Jaszczak was named the inaugural appointee to this newly endowed position.


“I thoroughly enjoy working with a great team of people and this world-famous collection of minerals.” —John Jaszczak
“As museum manager, Patty helps lead a great team of staff and students to deliver a top-notch experience for museum visitors. She also assists me with programming, collection care, and exhibits,” notes Jaszczak.
An affiliated Professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Jaszczak also serves as the associate director of education and outreach of MuSTI, the Multi-Scale Technologies Institute at Michigan Tech. MuSTI’s mission is to create knowledge and technologies leading to functional systems that incorporate nanotechnologies and microtechnologies, and to disseminate knowledge through research, scholarship, and education.
Dr. Jaszczak even has a mineral named in his honor, jaszczakite. It was discovered and named by Luca Bindi and Werner Paar in 2016. Jaszczakite consists of layered sulfide of lead, bismuth and gold from the Nagybörzsöny gold deposit in northern Hungary.
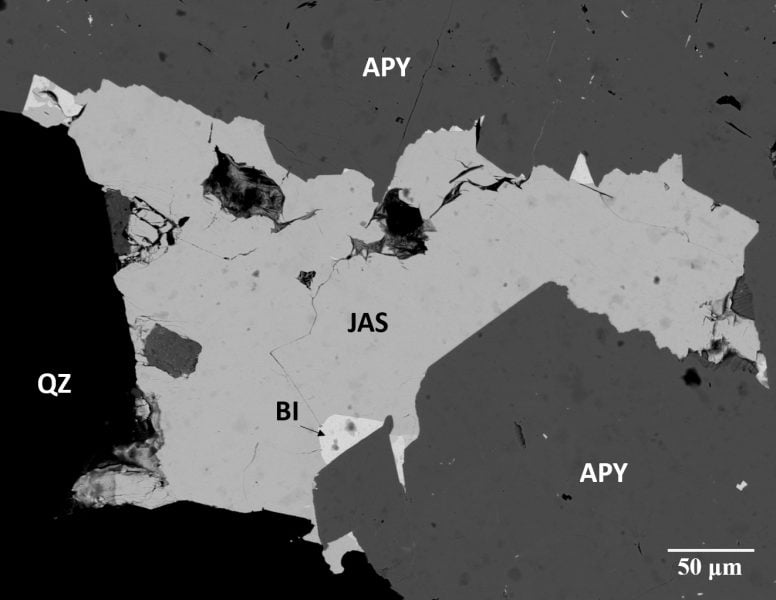

“Those who describe new minerals also can name them within guidelines and need to have the mineral (science) and proposed name approved by the International Mineralogical Association’s Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification. They can be named for chemistry, locality, etc. or to honor people (not relatives). “In this case, it was an honor that Luca Bindi initiated,” Jaszczak explains. “Luca and I have collaborated on characterizing and naming two new minerals. One, merelaniite, was just getting finished up at the time he found jaszczakite.”
The paper says:

Jaszczakite is named in honour of John A. Jaszczak (b.
1961), Professor of Physics at the Michigan Technological
University, and Adjunct Curator at the A.E. Seaman
Mineral Museum, and well-known mineral expert for
more than 30 years. His studies on the complexities of the
morphology and structure of natural graphite are of wide
international recognition.
Jaszczak together with Curator Emeritus George Robinson discovered very rare naturally occurring conical graphite on the surfaces of unusual graphite spheres at an occurrence in Ontario. One of their scanning electron microscope images of the tiny cones appeared on the cover of the journal Carbon in 2004 and 2005.
Prof. Jaszczak, how did you first get into science and engineering? What sparked your interest?

I became interested in being a scientist at a young age due to my interest in minerals and mineral collecting. That led me first to chemistry, and then to physics. I didn’t know about materials science and engineering until college and I stuck with physics, but am also proud to be affiliated with the Michigan Tech MSE department. So I’m not an engineer, but in my career I’ve helped to teach a lot of them about introductory physics!
I’ve been affiliated with the A. E. Seaman Mineral Museum since 1992 (adjunct curator) soon after arriving at Tech. It is a thrill to have become director and curator of this amazing collection.
Hometown, family?
I grew up in Parma, Ohio, near Cleveland. My wife and I met at Ohio State University while I was in graduate school. We’ve raised seven children here in Copper Country, including three Michigan Tech grads, and are now also enjoying grandchildren..
What do you like to do in your spare time?
My specialties include collecting graphite (pretty odd for a mineral collector) and collecting minerals from the Merelani gem mines in Tanzania. (I actually helped describe two new minerals from the Merelani mines.) I also enjoy photographing minerals. I’ve have had photos published in several mineral-related journals. My wife and I also regularly serve in our local church.

Patty, how did you first get into mineralogy? What sparked your interest?
I have long been mesmerized by minerals. I don’t really recall when I was not happy to add another piece to my collection. My interest only further developed in college, when I began to study geology.
Hometown and family?
I grew up in Connecticut, and received my undergraduate degree from Mount Holyoke College in Massachusetts. I first came to Michigan Tech for the Peace Corps Masters’ International Program, during which I served in Guatemala while earning my MS in Geology.
Any hobbies or pets? What do you like to do for fun?
My partner and I have two dogs, so we enjoy taking walks with them.
Read more:
Treasured Legacy, Bright Future for Renowned MTU Mineral Museum
Merelaniite Named Mineral of the Year
An element of Nobel-ity: Michigan Tech’s carbon connection
Watch
Watch this Mineral Museum mini-tour from Keweenaw Convention and Visitors Bureau to learn more about the museum’s history and collections.