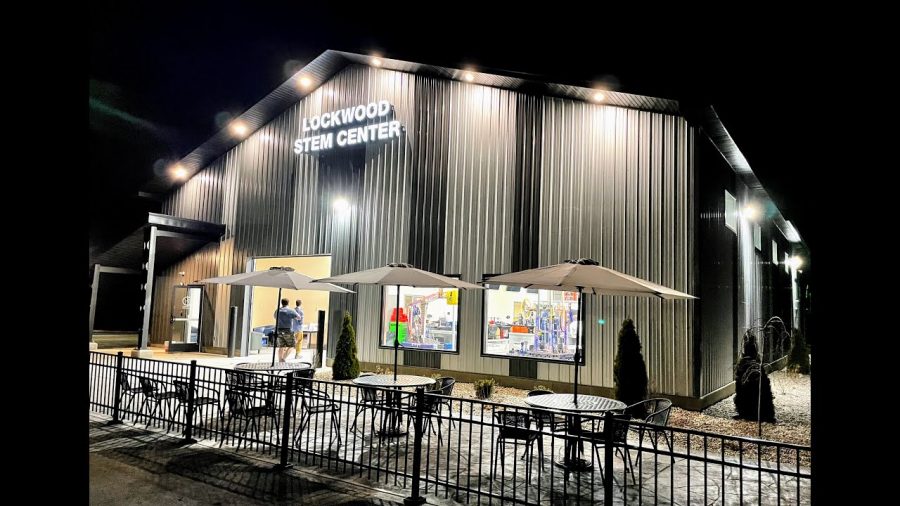
This month, Michigan Tech launched a partnership with the Lockwood STEM Center, part of Hemlock Public Schools in Hemlock, to provide educational outreach and opportunities to its students.
As part of the partnership, Michigan Tech established a scholarship program for Hemlock students who participate in robotics activities while in high school and then enroll at Michigan Tech as first-year students. The award provides $1,000 and is renewable annually. Two students will begin receiving the scholarship in Fall 2022 (still to be announced).

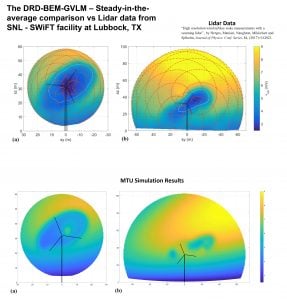
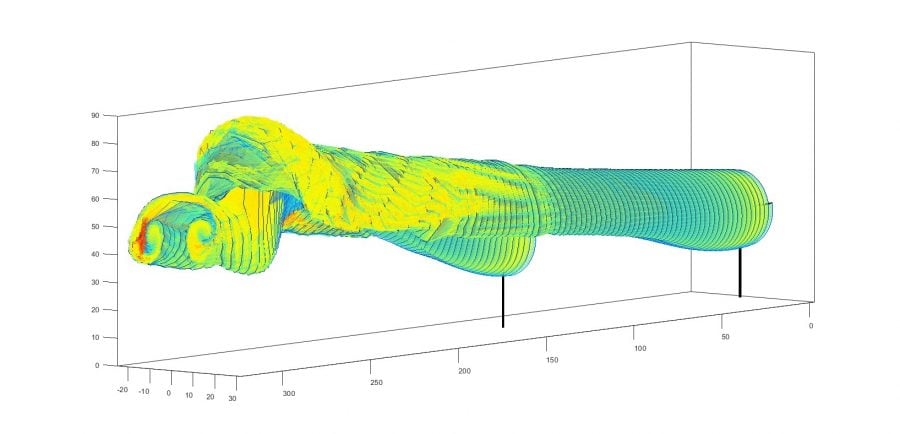
At Michigan Tech a variety of options exist for students who want to pursue robotics. The University also has a new BS in Robotics, in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Several Enterprise teams are focused on Robotics, including the Robotics Systems Enterprise, advised by Michigan Tech Professor (and alumnus) Jeremy Bos.
“Our partnership with the Lockwood STEM Center is in recognition of the incredible academic opportunities it provides to Hemlock Public School District students. We are thrilled to show our support for the Hemlock community and Great Lakes Bay region,” said Cassy Tefft de Muñoz, Executive Director of Enrollment Initiatives at Michigan Tech.

The Lockwood STEM Center was the vision of Tom and Dana Lockwood, teachers at Hemlock High School (HHS) who sought to advance STEM educational opportunities in the community. The state-of-the-art facility is truly a community effort with support from local individuals, industry and Hemlock Public Schools.
Former HHS student Gary Gariglio earned two bachelor degrees at Michigan Tech—one in electrical engineering (’86), and the other in business (’87). He is now president of Interpower Induction in Almont, Michigan. He delivered a keynote address to students and attendees during a special event on May 4 celebrating the new partnership. Gariglio highlighted the value of his Michigan Tech education and emphasized the importance of perseverance in the face of adversity—giving special acknowledgement to Matt Pumford and Greg Turner of Pumford Construction for their commitment and support in the oversight and construction of the Lockwood STEM Center. Pumford earned his bachelors degree in civil engineering at Michigan Tech in 1988.
The collaboration with Hemlock Public Schools is a continuation of Michigan Tech’s strong presence in the Great Lakes Bay Region. This includes a longstanding partnership with Hemlock Semiconductor supporting educational outreach and student attendance at Michigan Tech’s Summer Youth Programs (SYP).
Michigan Technological University is a public research university founded in 1885 in Houghton, Michigan, and is home to more than 7,000 students from 55 countries around the world. Consistently ranked among the best universities in the country for return on investment, the University offers more than 125 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in science and technology, engineering, computing, forestry, business and economics, health professions, humanities, mathematics, social sciences, and the arts. The rural campus is situated just miles from Lake Superior in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, offering year-round opportunities for outdoor adventure.
Read More
Jeremy Bos: What’s Next After First?
STEM Center Named: See photos and learn more about the new Lockwood STEM Center.
Registration for Michigan Tech’s Summer Youth Programs is open and more information is available at mtu.edu/syp.