The 2023 Annual Society of Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration (SME) Conference & Expo, held February 26–March 1 in Denver, Colorado, was a huge success for the Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences (GMES) at Michigan Tech. A large group of students and faculty representing the mining engineering and geological engineering programs attended the event, including eight BS students, five MS students, and a PhD student, along with two faculty members. They presented their research, received awards, and connected with alumni and industry.
The students in attendance were Michael Carly, Kolby Carpenter, Leanne Daanen, Jack Hawes, Jake Maxon, John Myaard, Jared Searl, Max Stange, Charles Addai, Ian Gannon, DharmaSai Eshwar Reddy Sirigiri, Enoch Nii-Okai, Emmanuel Wolubah, and Abid Danish.
Research Presentations
Associate Professor and Witte Family Endowed Faculty Fellow in Mining Engineering Snehamoy Chatterjee, delivered an oral presentation titled “Workers’ Compensation Data Analysis to Characterize Injury Severity in the Mining Industry,” based on his ongoing NIOSH-funded research.
Dr. Chatterjee’s MS student DharmaSai Eshwar Reddy Sirigiri gave an oral presentation titled “Modeling the Number of Days Lost from a Mining Accident by a Two-Stage Hierarchical Machine Learning Approach and MSHA Accident Data.”
Dr. Chatterjee’s PhD student Abid Danish presented a poster titled “Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning-based approach for clustering analysis of mining accident narratives.”
Recognitions
Dr. Nathan Manser, professor of practice in mining engineering and the chair for the Upper Peninsula Section of SME, accepted the Miners Give Back Award on behalf of the Upper Peninsula and Wisconsin SME local sections. This award is given annually and recognizes extraordinary achievements in community service and the advancement of the strategic objectives of SME during the past year by the local section membership. The focus of their work involved a collaboration with 4H to promote geosciences to middle-school-aged children in the region.
Alumni Connections
Michigan Tech alumni have always had strong representation within SME. Most notably, Marc LeVier (MTU BSMY ’71, MS ‘77) became the 2023 SME President on March 1 at the conclusion of SME Annual Conference & Expo.
As part of the week-long activities at SME, the GMES department hosted an alumni engagement event in the Hyatt Regency Downtown. About 66 guests attended the two-hour social event, including alumni from several MTU departments such as GMES and the Departments of Chemical Engineering, Materials Science and Engineering, and Civil, Environmental, and Geospatial Engineering.
The attendees came from classes in the mid-1980s through our most recent graduates, showcasing the vast network of connections alumni have, especially in the geoscience and minerals industries. A few members of the Industrial Advisory Board for Mining Engineering at MTU attended the event to rekindle connections with students and alumni. Our special thanks to Julie Marinucci for helping with the event organization! The event was a great opportunity for everyone to network and catch up with old friends. Overall, the alumni engagement event was a success, and plans for the next meeting in Phoenix are already underway. We are grateful to all the alumni who attended and look forward to seeing even more of them at future events.




Fun
The MTU Student Chapter of SME participated in the Komatsu Student and Professor event at the conference, a dueling-piano themed event with over 300 attendees from schools worldwide.

Other SME Activities
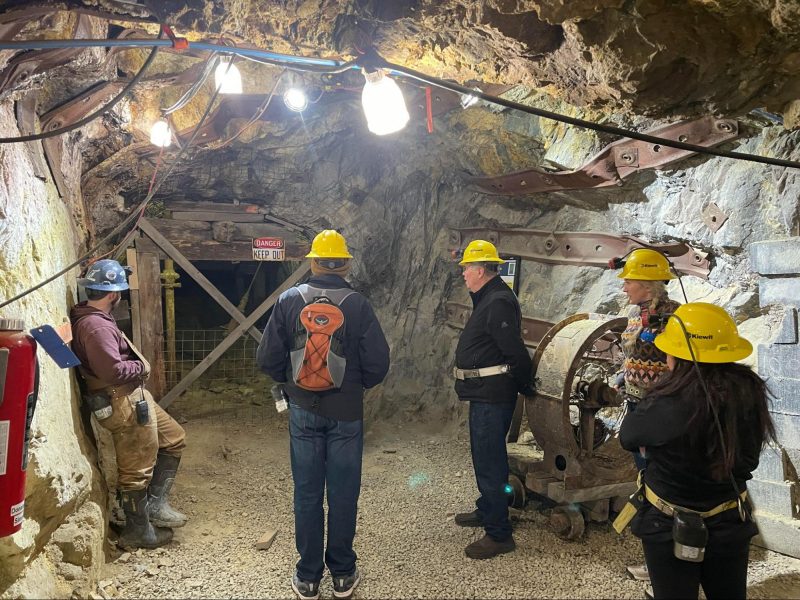
Director of MTU Mine Safety Program (hosted at GMES) Matt Portfleet, joined by mine safety trainers Marisa Roerig, Ron Gradowski, and Jake Drenth, also attended the SME conference. They had great opportunities to meet others within the mining industry and to exchange ideas. Michigan Tech Mine Safety also had the privilege of taking a two-hour private tour of the Colorado School of Mines “Edgar” mine. This is strictly an educational and research mine, which is operated by the school to provide students with hands-on experience and a location for research projects.
Says Matt Portfleet: “It was great to hear firsthand from our graduate student tour guides about the activities taking place there. Following this, we visited the Capitol Prize gold mine to experience some of the history of the area.”
The last day of our trip was again spent at the Colorado School of Mines, this time with Korky Vault, a 25-year veteran of mine safety training and specialist on cognitive impairments caused by sleep deprivation, substance abuse, and other influences. “This training provided us valuable knowledge and resources to share with our Mine safety trainees here in Michigan.”

Impact
We thank the Richard Saccany Mining Program Fund, the Robert Hendricks Mining Endowment Fund, and all our friends who contributed to the Mining and Material Processing Engineering Fund. Their contributions made it possible for our students to attend the SME conference and gain exposure to the latest advances in mining engineering research and practice, network with industry professionals, and explore future career paths.
As the department chair, I cannot overstate the importance of attending professional meetings for our students’ career development. The in-person attendance of the SME Conference & Expo was crucially important for building their professional networks and gaining valuable insights into the latest developments in the field. I believe that these experiences will contribute significantly to their success in their chosen careers.
One student attendee, John Myaard, shared: “I learned a lot and made some great connections with people in a diverse range of industries like mining, research, and mineral processing.”
Overall, the participation of our department in the 2023 SME Conference & Expo was a great success, and we look forward to participating in future events.
By Aleksey Smirnov, chair of GMES.