Michigan Tech recently launched a year-long Career and Technical Education (CTE) program for high school juniors or seniors in the area of Mechatronics. The new CTE Mechatronics program is offered through a partnership between Michigan Tech and the Copper Country Intermediate School District (CCISD).
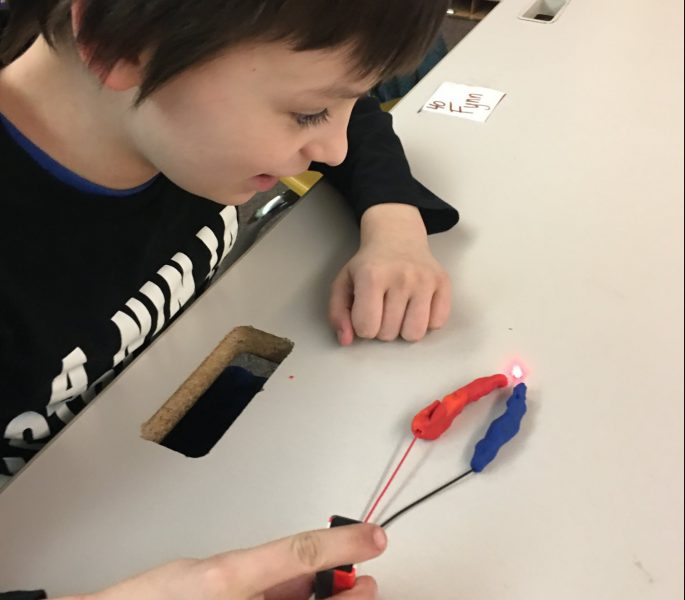
Mechatronics uses electromechanical systems, typically automated for the design of products and processes. Industry 4.0—sometimes called the “fourth industrial revolution”—applies various aspects of mechatronics to manufacturing enterprises. Topics in the CTE Mechatronics program include; automation, computer integrated manufacturing, high speed manufacturing, embedded systems design and controls, industrial robotics, pneumatics, hydraulics, and computer-aided design.
“Students in the program will find careers in smart manufacturing fields, or they can find a pathway at Michigan Tech into undergraduate or graduate degrees in Engineering Technology, Engineering, or Mechatronics.” says John Irwin, chair of the Department of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Technology.
Teaming up to deliver the instruction are faculty in the Mechatronics, Electrical and Robotics Engineering Technology (MERET) program in the College of Computing, and faculty in the Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Technology (MMET) Department in the College of Engineering.
There are 10 students enrolled this fall 2020 from the local area school districts of Houghton, Hancock, Calumet, and L’Anse. CTE Director Shawn Kolbus expects the program to only increase in popularity. “Local business owners approached us last year wanting to get more students from the area interested in Mechatronics, CADD and Engineering,” he says. “The result was the Mechatronics program which encompasses standards from each area.”
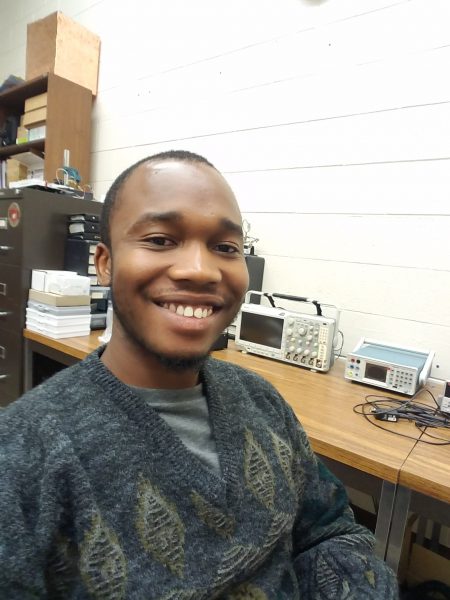

The course is taught by two mechatronics professionals who possess both industry and teaching experience. One of those instructors is George Ochieze, who is pursuing a master’s degree in Mechatronics and a PhD in Mechanical Engineering at Michigan Tech. “Even in difficult times during the pandemic, these young scholars show overwhelming potential to conquer the mechatronics field—a glimpse into a welcoming future in engineering,” says Ochieze.

The second instructor, Chinmay Kondekar, will earn an MS in Electrical Engineering at Michigan Tech in 2021. “Teaching for local schools is an opportunity for me to give back to people in the community who welcomed me as an international student,” says Kondekar. “I hope to create a strong interest in robotics and automation in my students. People with these skills will be the future of manufacturing and will have plenty of opportunities.”
Program enrollment is closed for 2020, but will be available again starting in fall 2021. This spring there will be the opportunity for area sophomore and junior students to visit Michigan Tech to tour the labs and meet the instructors. Both the Applied Computing and MMET department labs used at Michigan Tech are equipped with state-of-the-art electronics and mechanical systems partially provided through generous startup funding from the CCISD.
For more information please contact Shawn Kolbus, Director, Career and Technical Education, Copper Country Intermediate School District (906) 250-5353.
Michigan Tech faculty administering the CTE program include Prof. John Irwin, Chair of the Department of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Technology, or Prof. Alex Sergeyev in the College of Computing.