“We had a problem, a goal, and a few problems.”
-Tyler Walczak
We are pleased to present this guest blog post by Lynn Jarvi. She serves as a Construction Supervisor for Copper Country Habitat for Humanity. In March 2025, she earned her Green Belt certification, demonstrating a strong foundation in continuous improvement principles. In this blog, Lynn discusses a recent project where she worked alongside students from Ferris State University’s School of Business, aimed at streamlining the volunteer paperwork process.
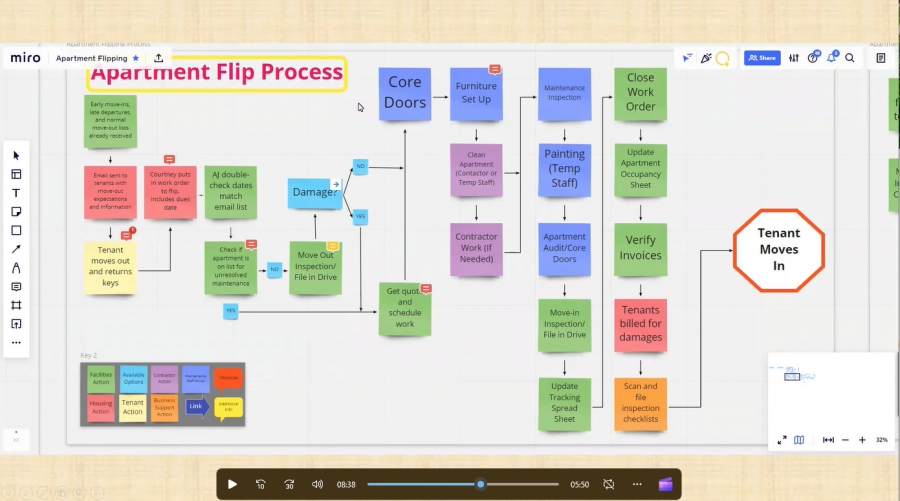
As one of two Construction Supervisors for Copper Country Habitat for Humanity, I was frustrated by issues with volunteer paperwork. We rely on volunteers to help build our houses, and each one must fill out paper forms at the jobsite before starting work.
This system bugged me. We had to make sure forms and pens were always available, there were delays while people filled them out, the information had to be transferred manually to a spreadsheet back at the office, and there was a risk of exposing private information.
While working toward my green belt certification through Michigan Tech’s Office of Continuous Improvement, one of our group projects was to co-facilitate a small kaizen event. Our group chose to take on the Habitat’s volunteer form process.
Thanks to a group member’s suggestion, we were able to hand this improvement project over to students from Ferris State University’s School of Business to carry it across the finish line. They facilitated their own kaizen event, meeting virtually over several weeks with Habitat’s administrative assistant, a volunteer, and me, going to the Gemba with us online. Ultimately, they developed a plan to digitize the volunteer forms.
We’re grateful to MTU’s Office of Continuous Improvement and Ferris State’s School of Business for generously sharing their Lean expertise to further Habitat for Humanity’s mission of providing affordable housing to our community, one kaizen project at a time.
Watch this continuous improvement journey by clicking on the video below!
Want to learn more about Continuous Improvement and see more videos like this one? Visit our YouTube channel by clicking on this link!