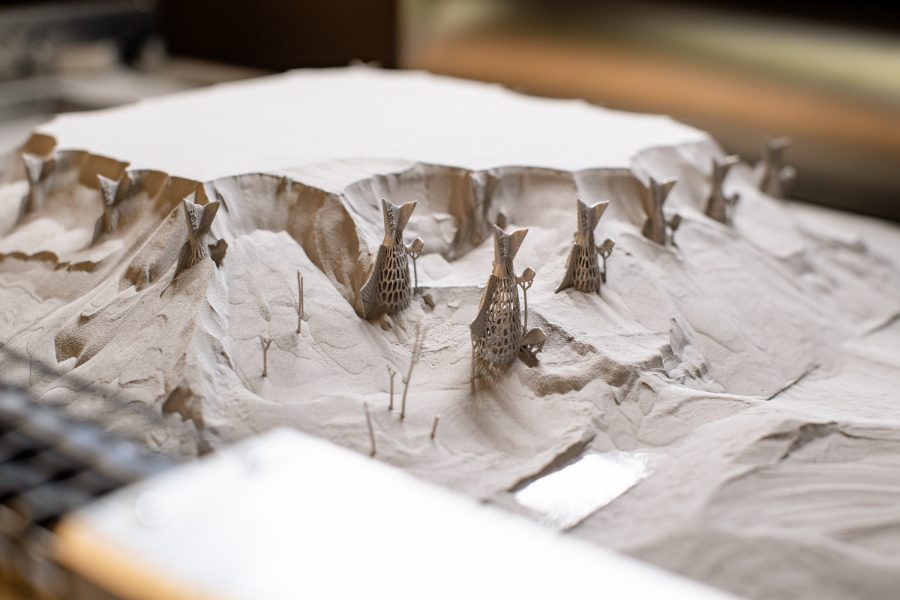
A gift from Alumni, Michigan Tech’s highly-advanced 3D metal printer—a 3D Systems ProX350—arrived last March. It’s now up and running, able to process 11 unique metals, including bio-grade titanium (for biomedical applications), cobalt and chromium, several types of stainless steel, and more. With a resolution of 5 microns, this new large printer is state-of-the-art.
Obtaining the new 3D printer was made possible by the generosity of Michigan Tech alumni. ME-EM Department Chair Bill Predebon received a 20 percent discount on the $875K system from Scarlett Inc. The owner of Scarlett Inc, Jim Scarlett, is a mechanical engineering alumnus.
In addition to Scarlett, several other alumni donors pitched in. One anonymous donor provided over $600K , and five others have made up the difference to meet the full cost of $673K. Those five are: Ron Starr, John Drake, Frank Agusti, Todd Fernstrum, and Victor Swanson.

“Very few universities have a 3D metal printer of this quality and versatility,” says Predebon. “It is one of the most accurate metal 3D printers available. With approximately a 1-ft. cube size billet, which is an impressive size billet, you can make a full-size or scaled-down version of just about anything,” says Predebon.
“We can use our own metal powders, as well,” adds Predebon. “That’s a huge plus. Michigan Tech researchers, particularly those focused on materials development, can use the printer to deposit experimental metal compositions to produce unique metal alloys customized specifically for the 3D printing process.”
Faculty and graduate students at Michigan Tech will have access to the 3D metal printer for research projects. Undergraduate students working on senior design projects and student-run Enterprise teams will, too.
The process is direct metal printing, or DMP, and it’s a type of additive manufacturing, Predebon explains. “You start with metal powders, and from those you create the final metal part. You’re adding a material—in this case, metal—bit by bit. Traditional manufacturing is all about subtracting: taking metal away to make a part. This is the inverse, and it’s a game changer. You can do so much more this way.”
“For many industries—including medical, automotive and aerospace—3D metal printing is a game changer. Here on campus it will be a game changer for Michigan Tech faculty and students, too.”
Very few universities yet have a system with this sophistication and quality, notes Predebon.
The benefit for Michigan Tech students, Predebon says, is competitive advantage. “When our students interview for a job, they will be able to communicate how they’ve been able to produce parts in a way very similar to what industry is doing. Some companies have metal 3D printers worth millions of dollars. In industry, engineers can use one of those to print out an entire engine block,” he says. “When Michigan Tech graduates see one on out in industry, the 3D metal printer might be larger, but they will already be familiar with the type of system.”
According to Materials Science and Engineering Professor Steve Kampe, development of additive manufacturing of metals represents a huge opportunity that will be prominent in manufacturing for generations to come. “It is a transformative technology in engineering,” says Kampe. “Using 3D printing to create metallic components poses huge challenges; but the potential benefits are enormous.”
“Metal additive manufacturing along with polymer additive processes are industry 4.0 topics included in Michigan Tech’s online graduate certificate in Manufacturing Engineering,” adds Professor John Irwin, chair of the Department of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Technology. “It is very fortunate for us to have this metal 3D printer here on campus. We’ll use it to demonstrate additive manufacturing design principles and view product purpose: form, fit, and function.
Michigan Tech’s new metal 3D printer is located on campus in the Minerals and Materials Engineering (M&M) Building. The location in Room 117, is near several other 3D polymer printers. For more information on using the new printer, contact MSE Research Engineer Russ Stein.