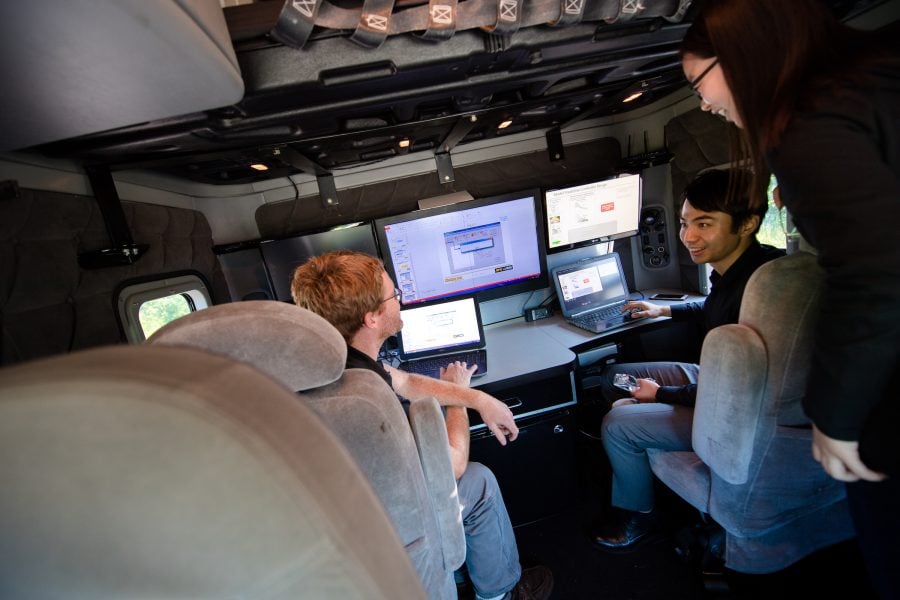
Bo Chen shares her knowledge on Husky Bites, a free, interactive webinar this Monday, November 15 at 6 pm ET. Learn something new in just 20 minutes (or so), with time after for Q&A! Get the full scoop and register at mtu.edu/huskybites.
What’s next, NEXTCAR? What are you doing for supper this Monday night 11/15 at 6 pm ET? Grab a bite with Dean Janet Callahan and Bo Chen, Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Electrical Engineering at Michigan Tech.
During Husky Bites, Prof. Chen and one of her former students, alum Dr. Joe Oncken, will share how engineers go about designing and creating the crucial elements of an all-electric vehicle ecosystem. Oncken earned his PhD at Michigan Tech—he’s now a postdoctoral researcher at Idaho National Lab.
Chen and her research team at Michigan Tech envision an all-electric future. They develop advanced control algorithms to build the nation’s electric vehicle charging infrastructure and highly efficient hybrid electric vehicles, integrating with advanced sensing technologies that allow for predictive control in real time. These technologies enable the kind of vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication that will reduce our nation’s energy consumption.

Throughout her career Chen has made major contributions in the field of embedded systems, developing cutting-edge applications for hybrid-electric and electric autonomous systems.
One of Chen’s courses at Michigan Tech, Model-based Embedded Control System Design, is regularly in high demand, not only by ME students but also EE students. “This is a testament to her teaching ability and the importance of the topic,” says ME-EM department chair Bill Predebon.
Chen’s Intelligent Mechatronics and Embedded Systems Lab is located on the 5th floor of the ME-EM building. But she spends a good deal of time working on NEXTCAR research at the Advanced Power Systems Research Center (APSRC), located a few miles from campus near the Houghton Memorial Airport.
“Vehicles that are both connected and automated—two paradigm-shifting technologies—will soon become vital for the improvement of safety, mobility, and efficiency of our transportation systems.”
In 2016 the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects-Energy (ARPA-E) awarded $2.5M to Michigan Tech for NEXTCAR research. The project—led by ME-EM Professor Jeff Naber as PI and Co-PIs Chen, Darrell Robinette, Mahdi Shahbakhti, and Kuilin Zhang—developed and demonstrated their energy reduction technologies using a fleet of eight Gen II Chevy Volt plug-in-hybrid vehicles (aka PHEVs).
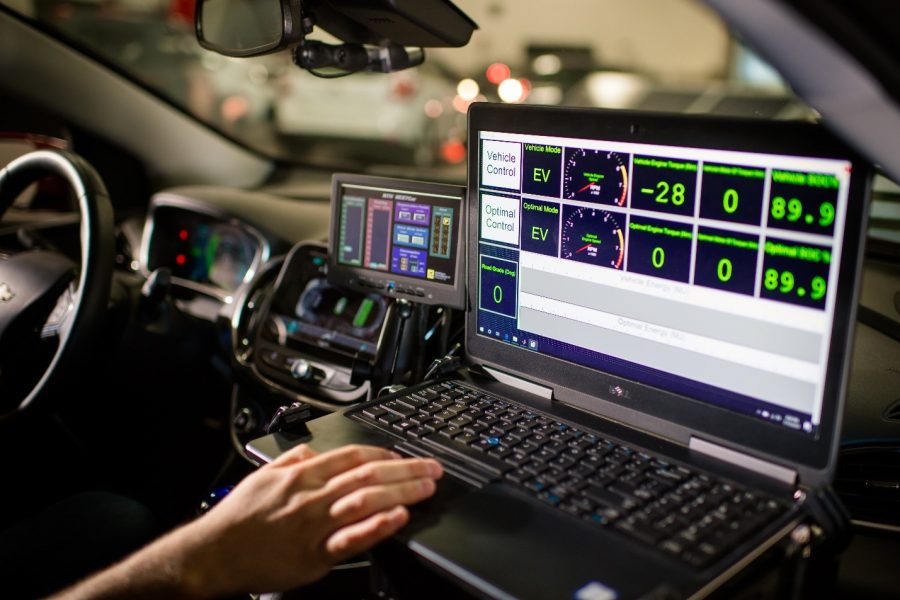
The team tested the fleet on a 24-mile test loop to showcase energy optimization, forecasting, and controls—including vehicle-to-vehicle communications.
“The rich information provided by connectivity—and the capability of on-board intelligent controls—are shifting the old way (reactive and isolated vehicle/powertrain control) to the new way (predictive, cooperative, and integrated vehicle dynamics and powertrain control),” Chen explains.

Oncken is a hands-on engineer, but not all of his graduate research at Michigan Tech was done under the hood of a hybrid-electric vehicle. In an effort to maximize fuel efficiency in the fleet’s Chevy Volts, he worked with Chen where the car’s digital and mechanical parts meet—powertrain control. He looked at future driving conditions, such as changing traffic lights, and modified the vehicle’s powertrain operation to use the minimum amount of fuel.
Working in Chen’s lab, Oncken used Simulink software to develop a model, specifically looking at predictive controller design. That means when a traffic signal turns red, a self-driving vehicle not only knows to stop, but also gets directions on the best way to slow down and minimize fuel use.
Oncken would simulate this in the Simulink model, embed the program into the Chevy Volt, then test it using five upgraded traffic signals in Houghton that rely on dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) to talk directly to the car’s programming.
By the end of the NEXTCAR project, the Michigan Tech team had achieved a 21 percent reduction in energy consumption.
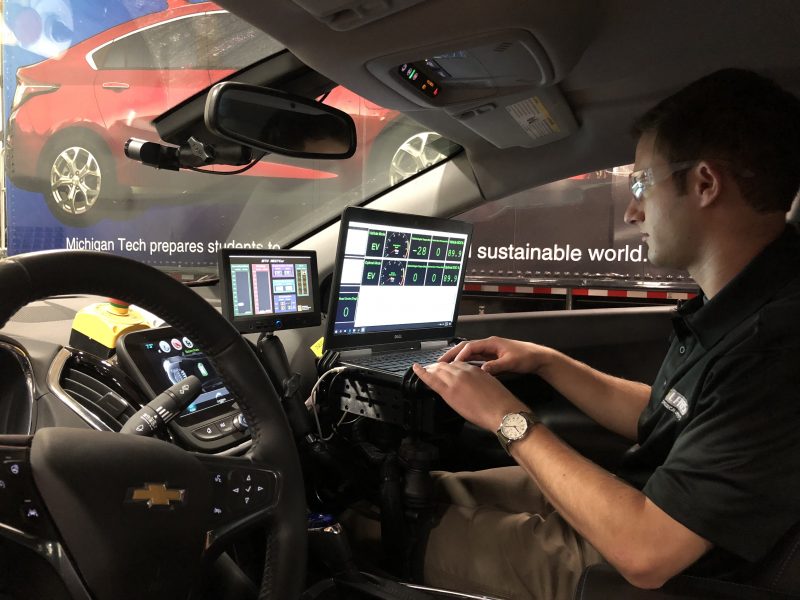


Now, with new funding from ARPA-E for NEXTCAR II, the team shifts to a broader application of vehicles with level 4 and 5 of autonomy. They will seek to reduce energy consumption by 30 percent this time in the hybrid Chrysler Pacifica and further apply the savings to the RAM 1500 and the Chevy Bolt—while also considering level 4 and 5 automation to gain efficiencies.
Naber and Chen, along with Grant Ovist, Jeremy Bos, Darrell Robinette, Basha Dudekula and several more graduate students now work together on NEXTCAR II with another round of funding worth $4.5M. They’ll maintain vehicles in multiple locations, both on the Michigan Tech campus and at American Center for Mobility (ACM) for road testing. ACM is a partner in the project, along with Stellantis and GM.
Prof. Chen, how did you first get into engineering? What sparked your interest?
I was attracted by the power of automation and controls. It is currently affecting every aspect of our lives. I want to make contributions specifically to advance the automation technologies.

Hometown, family?
I was raised in Shaoxing, Zhejiang province in China. I lived in Davis, California for 8 years while earning my PhD at the University of California-Davis. My daughter loves snowboarding and lives in New Jersey.
Dr. Oncken, where did you grow up?
I grew up with my parents and two sisters in Grand Forks, North Dakota. I earned my BS in Mechanical Engineering at the University of North Dakota in 2016. I came to Michigan Tech to earn my PhD soon after, and graduated in 2020.
How did you first get into engineering? What sparked your interest?
There wasn’t any one moment that made me decide to get into engineering. It was more of a process throughout my childhood. Growing up, I was always interested in how things work. My dad is very mechanically inclined so he was alway fixing things around the house and woodworking, so that launched my interest as a young kid. At that time he worked for John Deere, so I got to spend time sitting in tractors and combines, something that will spark any 5 year old’s interest in mechanical things.
In high school, I also worked for a John Deere dealer. Another job I had involved the technical side (lighting, sound, and set building) of theater and concert productions. While these may seem like two different worlds, they both gave me a behind-the-scenes look at how machinery and large technical systems operate. Together they made me want to pursue a career where I’d be the one designing how things work.
Finally, living in a university town, there were lots of opportunities to tour the University of North Dakota’s engineering school and see what students got to work on, opportunities that cemented my desire to go into engineering myself.

Any hobbies? Pets?
My main hobby is anything outdoors. I spend my free time mountain biking in the summer, skiing in the winter—and hiking when I’m not doing one of the previous two things.
I also really enjoy cooking and wood working. I don’t currently have any pets, but I did grow up with dogs. I will have a dog of my own sooner rather than later!
Read More
Power Grid, Powertrain and the Models that Connect ThemMichigan Tech Automotive Energy Efficiency Research Receives Federal Award of $2.8 Million from US Department of Energy